Explore Our Main Equipments
At Agarwood Research Website, we take pride in our state-of-the-art equipment, carefully selected to support our rigorous research and exploration of agarwood. Our cutting-edge tools enable us to delve deep into the complexities of this aromatic resin, unraveling its chemical composition and uncovering its medicinal and aromatic properties.
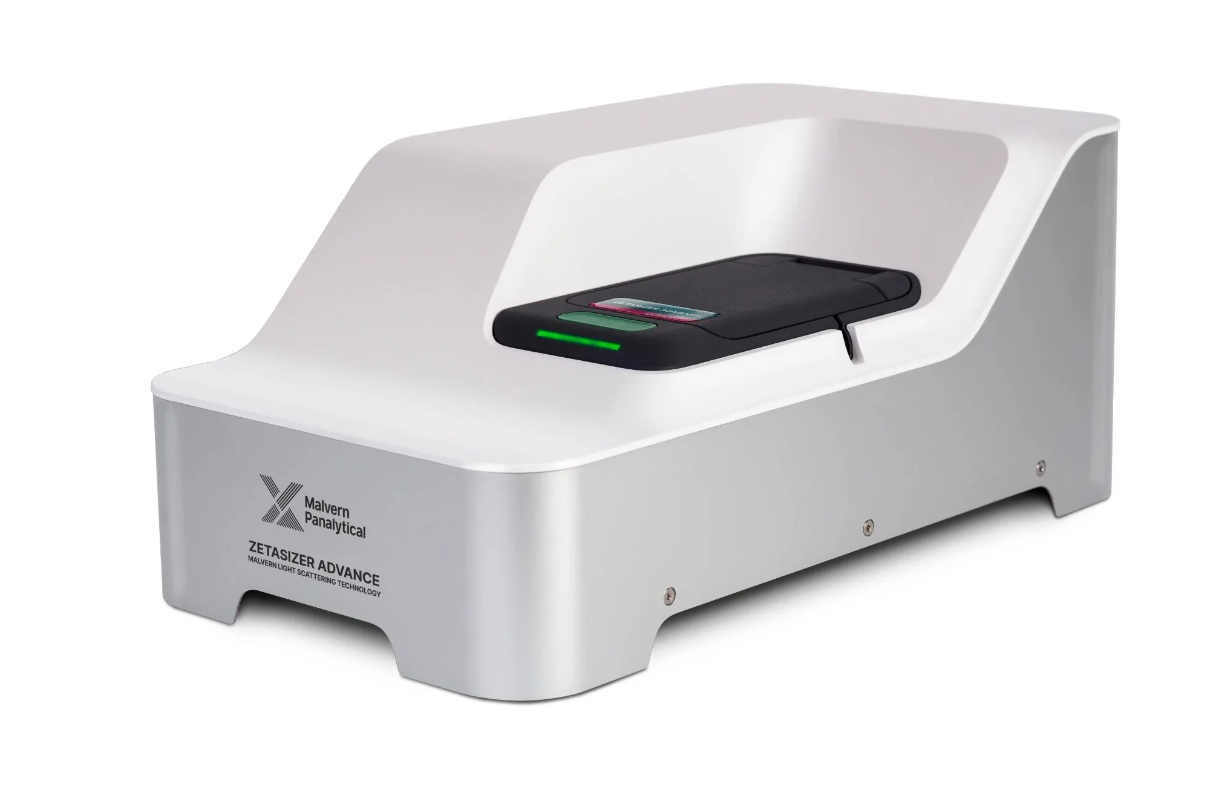
1.Dynamic Light Scattering Instrument
Dynamic light scattering (DLS), sometimes referred to as Quasi Elastic Light Scattering (QELS), is a non-invasive, well-established technique for measuring the size and size distribution of molecules and particles typically in the submicron region, and with the latest technology, lower than 1nm.
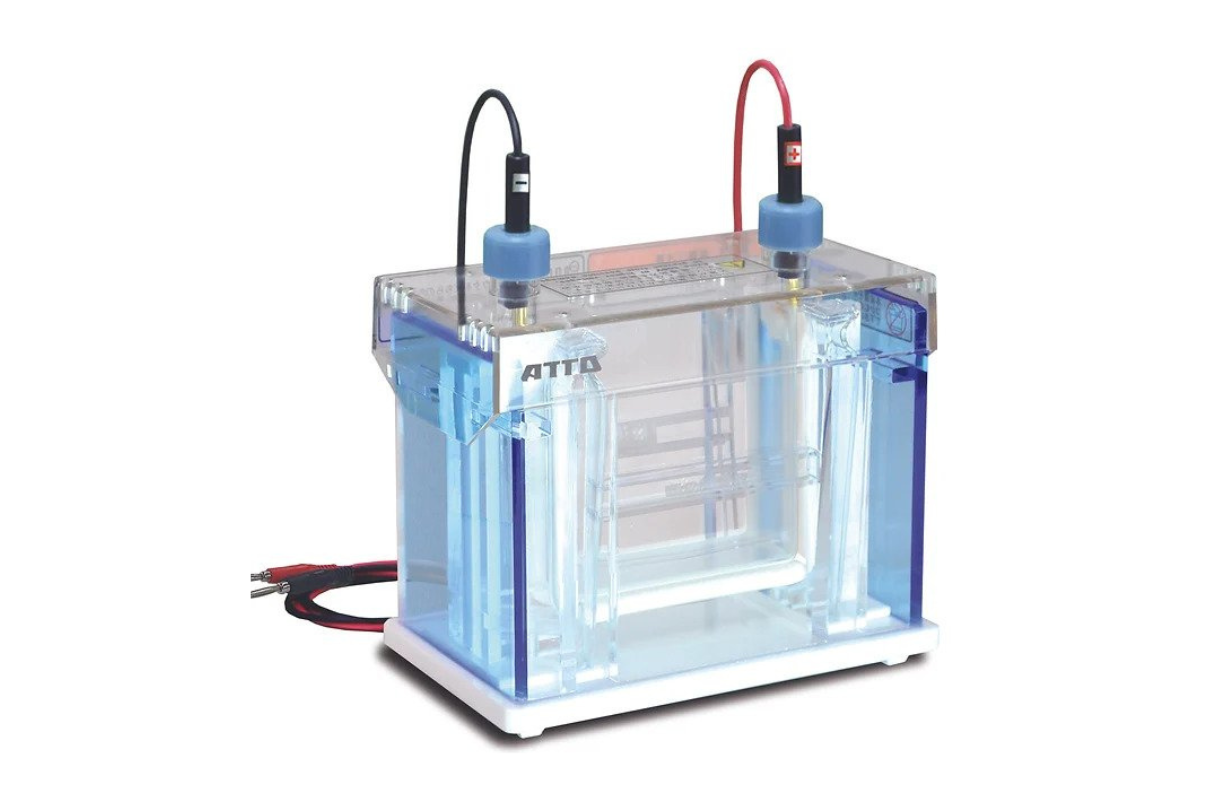
2.Electrophoresis System (Vertical, Horizontal and Power Supply)
An electrophoretic system consists of two electrodes of opposite charge (anode, cathode), connected by a conducting medium called an electrolyte. The separation effect on the ionic particles results from differences in their velocity (v), which is the product of the particle's mobility (m) and the field strength (E):
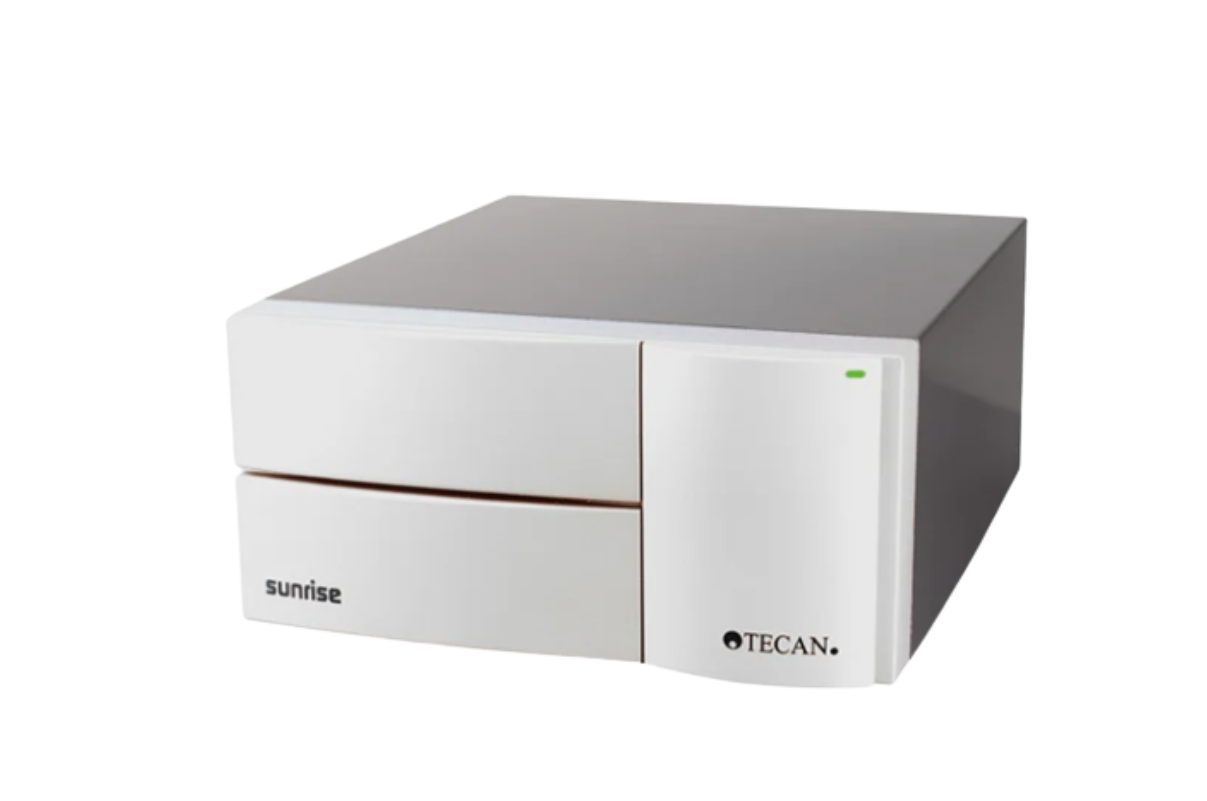

3.ELISA Reader Multimode
A multi-mode reader has many advantages for labs conducting applications ranging from ELISAs to nucleic acid and protein quantitation to cell imaging. Combining multiple microplate technologies and detection modes into a single, more versatile unit may be an ideal choice especially if you have limited lab space.
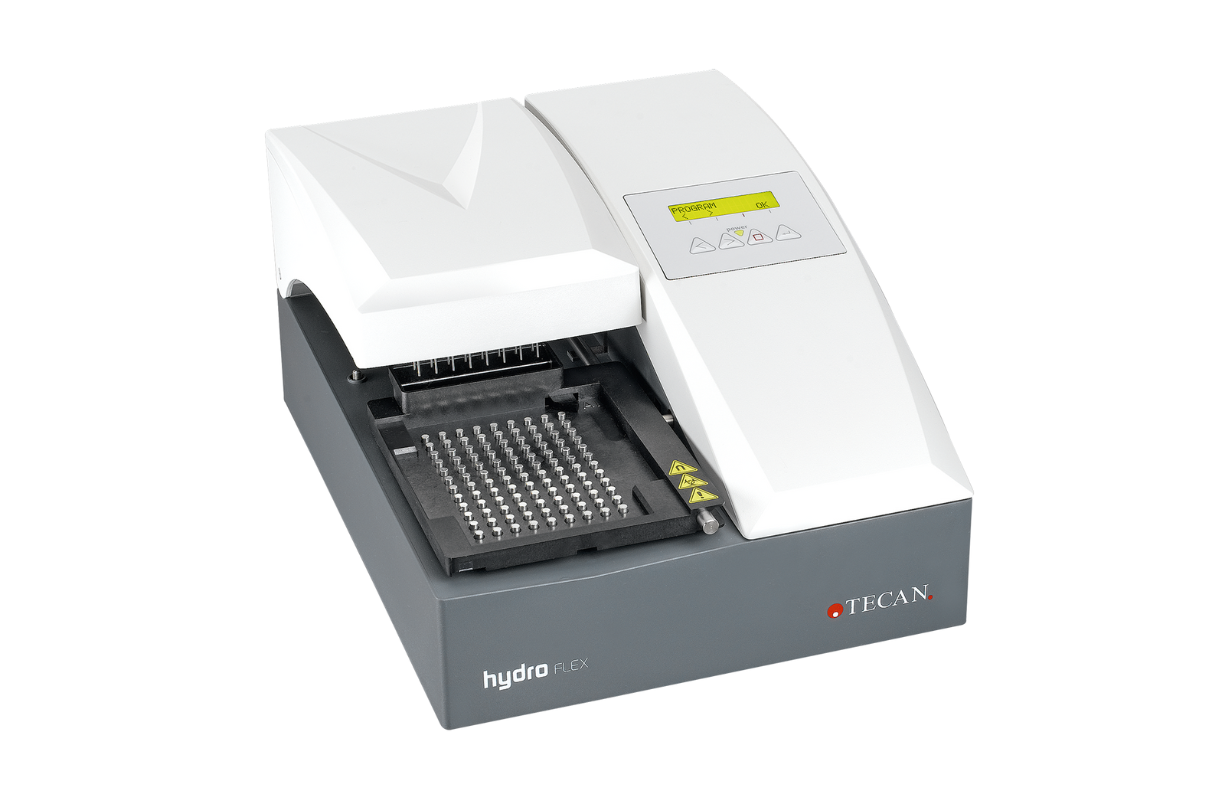

4.ELISA Washer
The ELISA Washer or Microplate washer is designed to wash the microwells as a part of the ELISA testing process. The performance of the ELISA test kits and reliability in their test results depend heavily on a good quality ELISA Reader and washer being used for performing the ELISA tests.

5.Gel Documentation System
Gel documentation systems, also known as 'gel docs' or 'gel imagers,' are used to record and analyze the results of gel electrophoresis and membrane blotting experiments. These instruments are necessary for visualizing stained or labeled nucleic acids and proteins in media such as agarose, acrylamide, or cellulose.
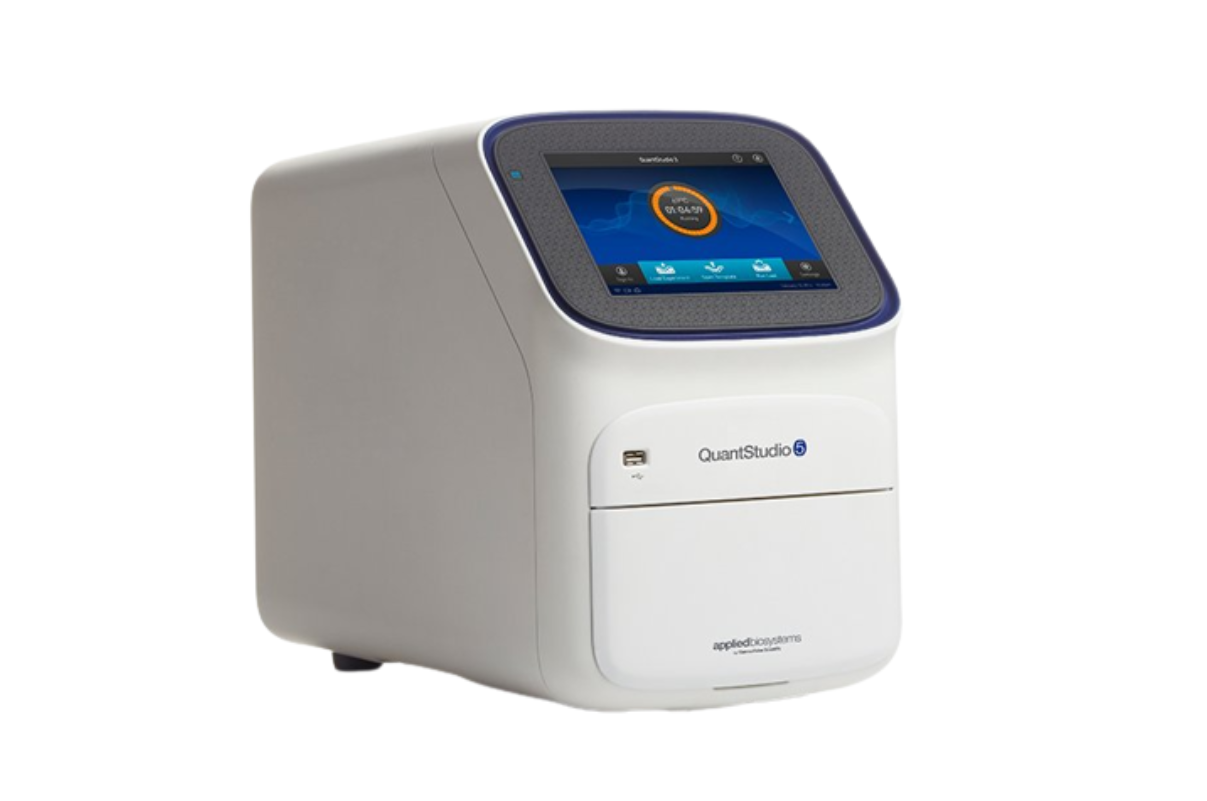
6.Real Time PCR Machine
In conventional PCR the amplified DNA product, or amplicon, is detected in an end- point analysis. In real- time PCR, the accumulation of revision product is measured as the response progresses, in real- time, with product quantification after each cycle.
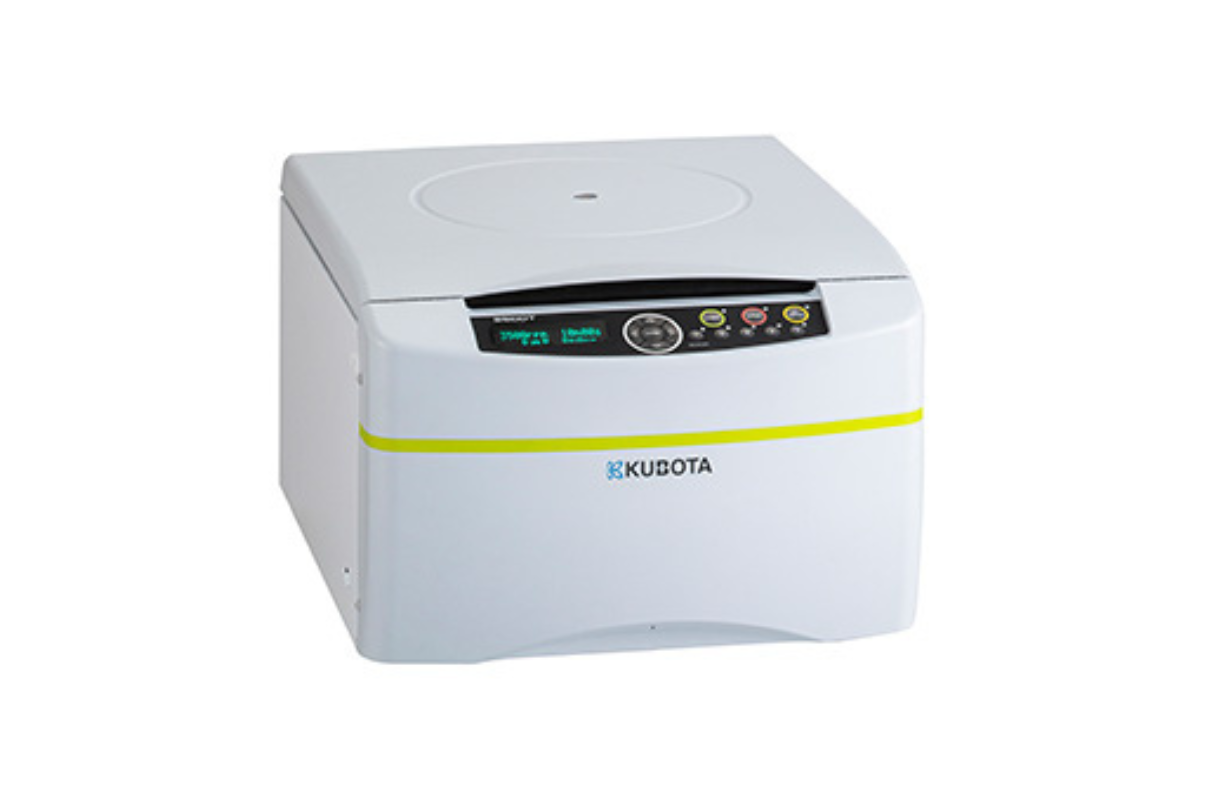

7.Centrifuge Machine (Benchtop)
Benchtop centrifuges are the equipment utilized in laboratories to separate and purify molecular mixtures in a liquid medium based on their density gradient. A tabletop centrifuge is a medium-capacity centrifuge used for the separation of milliliter heterogeneous mixtures or samples. This device works by spinning the samples loaded in various rotor types at high speed.
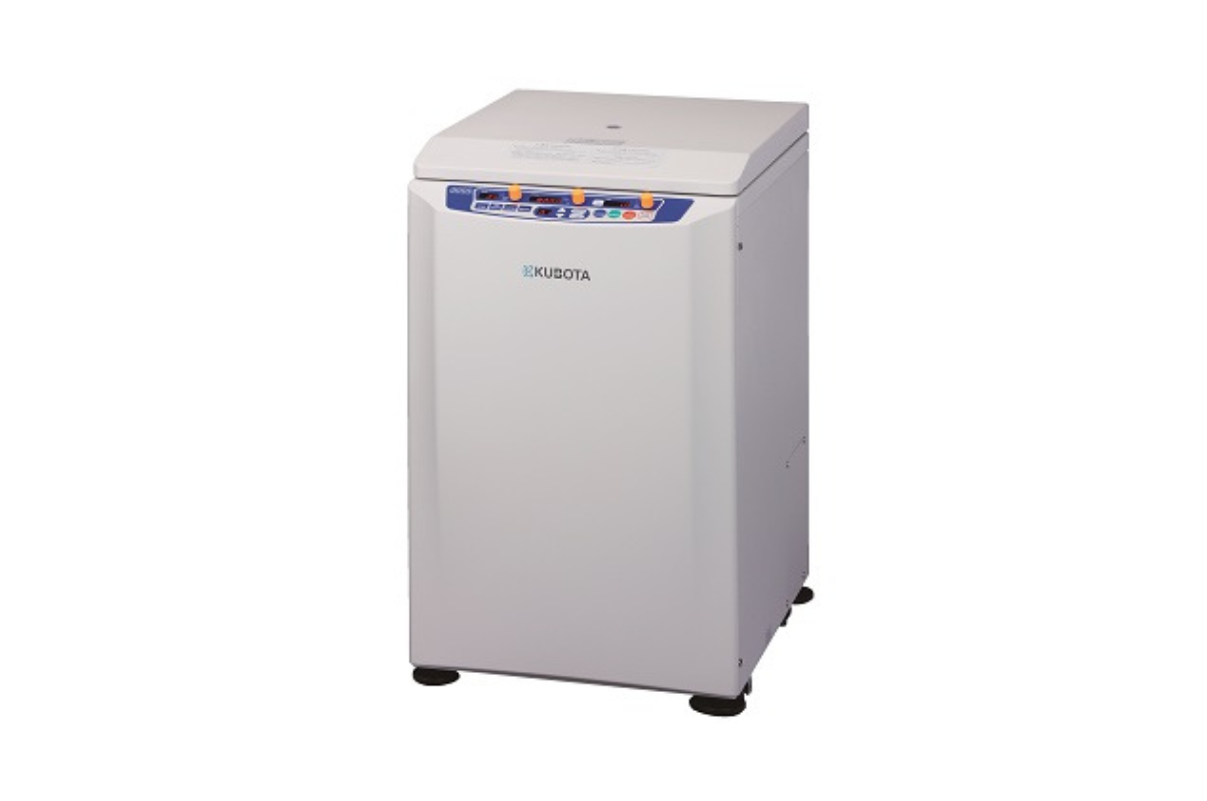

8.Centrifuge Machine Refrigereted High Speed
This is a device that is capable of separate any kind of samples, depending on your needs and tests. High Speed Refrigerated Centrifuge work by a separation method where the components of a sample are separated based on their density according to the centrifugal force they experience.
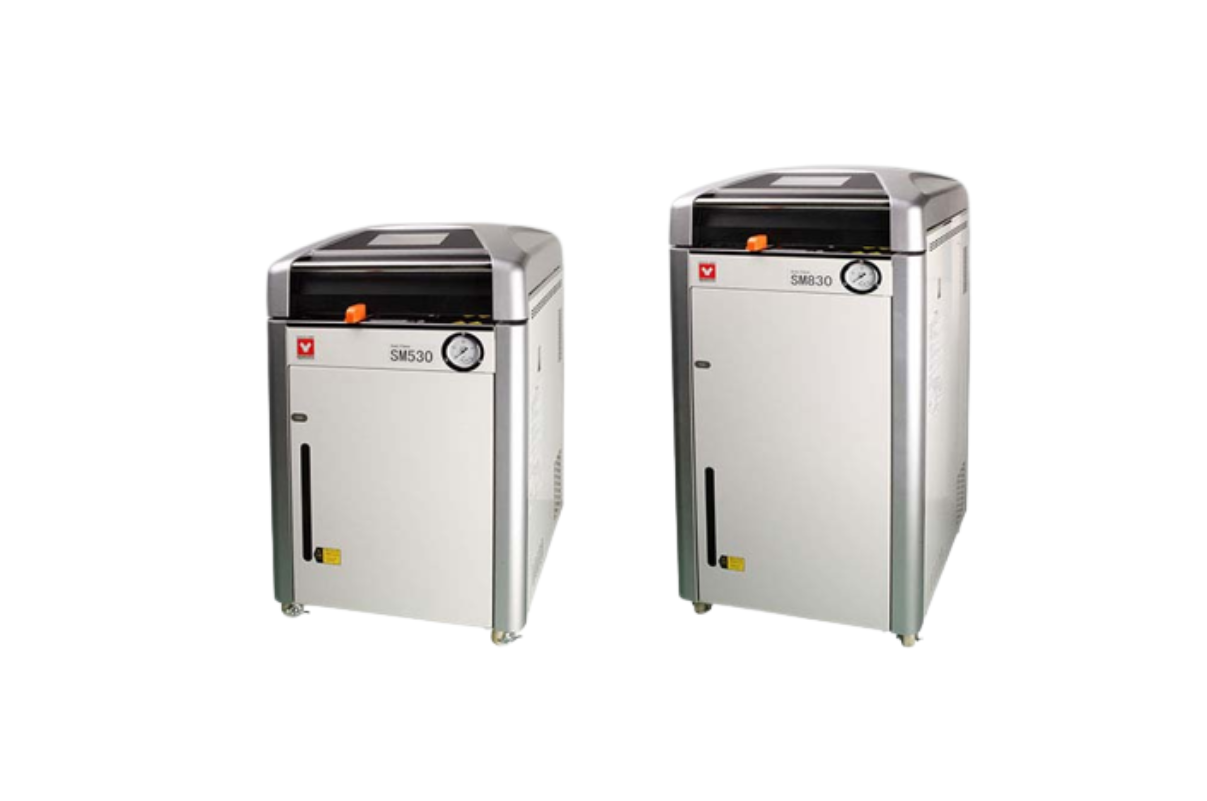

9.Autoclave (Steam Sterilizer)
Autoclaves are also known as steam sterilizers, and are typically used for healthcare or industrial applications. An autoclave is a machine that uses steam under pressure to kill harmful bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores on items that are placed inside a pressure vessel.
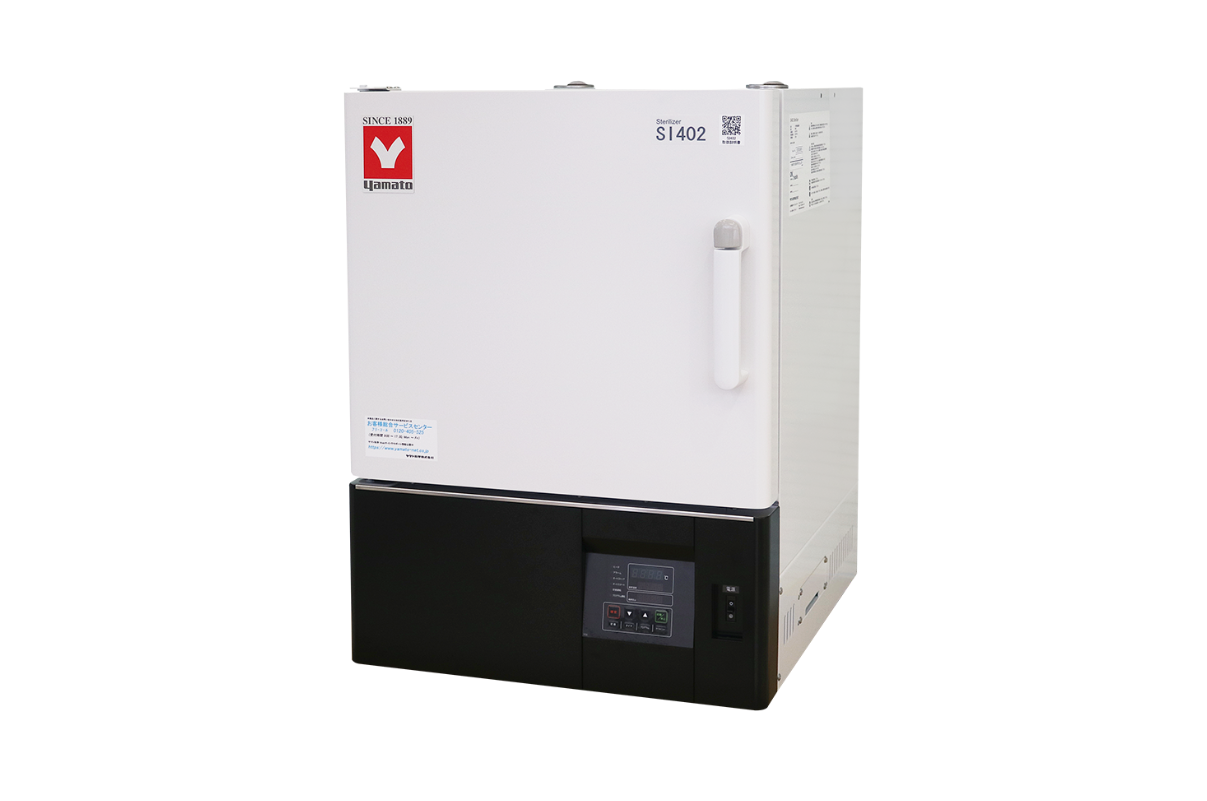

10.Autoclave (Dry Sterilizer)
Autoclave sterilization uses steam to sterilize instruments and equipment. This common method is a fast, efficient way to ensure instruments are properly cleaned. Dry heat sterilizers can sterilize dental tools without the use of steam, which is necessary for certain tools that might be damaged with moist heat.
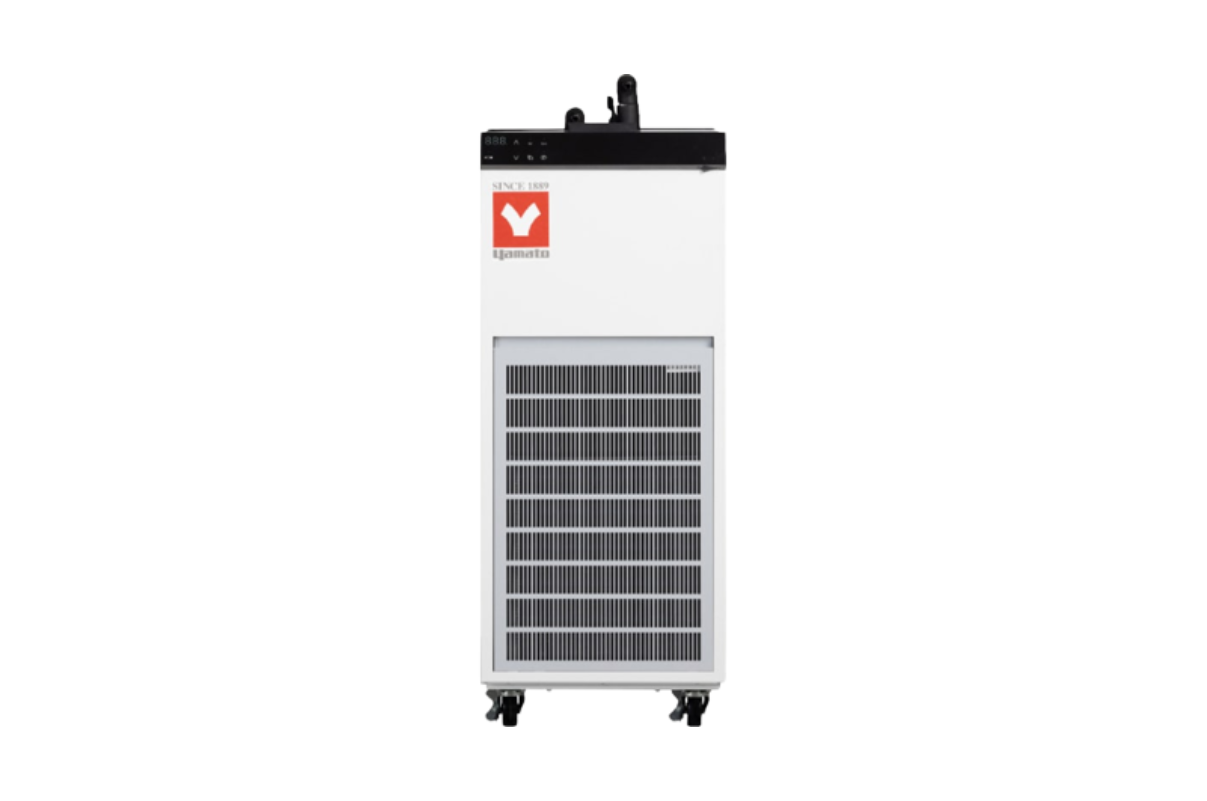

11.Chiller Cooling Water Circulator
A chiller is a machine that removes heat from a liquid coolant via a vapor-compression, adsorption refrigeration, or absorption refrigeration cycles. Recirculating chillers are used to cool laboratory equipment such as rotary evaporators. Chillers are available in a variety of cooling capacities, achievable temperature ranges, and reservoir volumes.
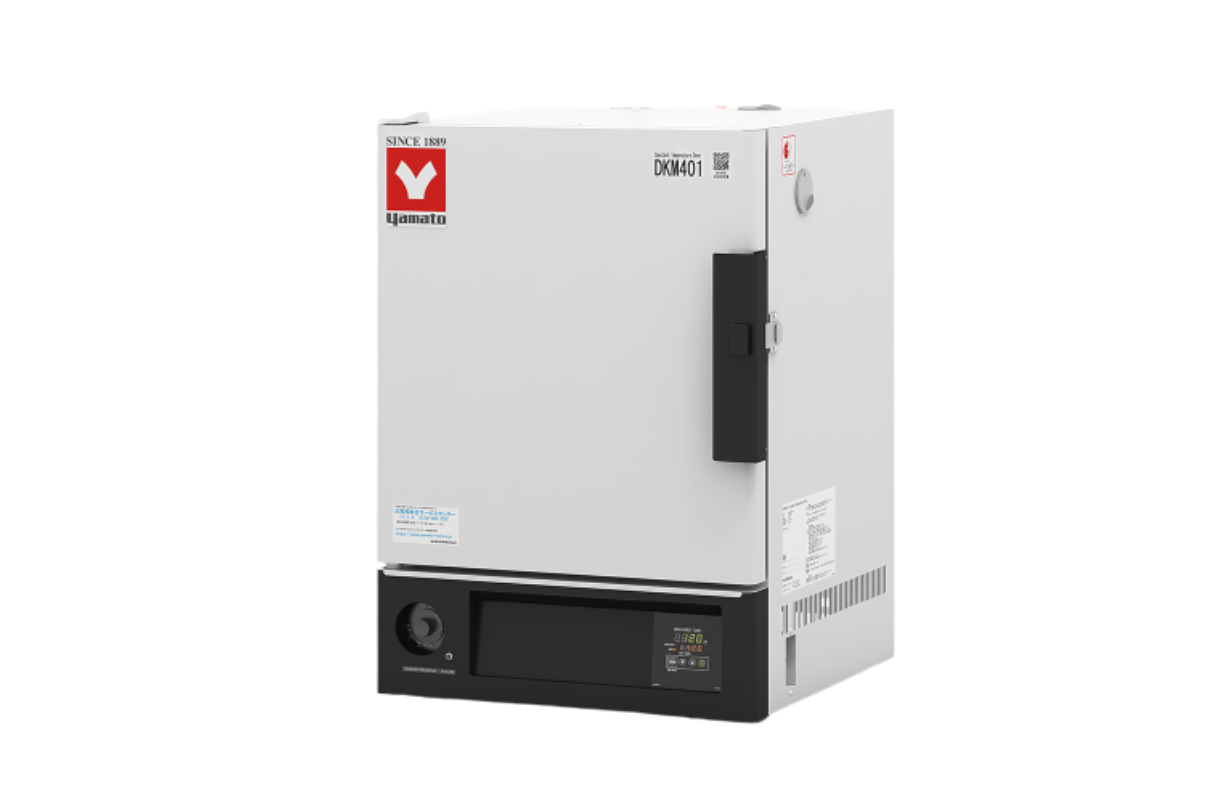

12.Drying Oven (Force Convection Economical)
Forced convection drying oven is commonly used in laboratories and manufacturing facilities for the purpose of sample drying and sterilization. Forced convection drying oven is built with a fan inside the wall of the oven which forces the hot air in the oven to circulate throughout it.
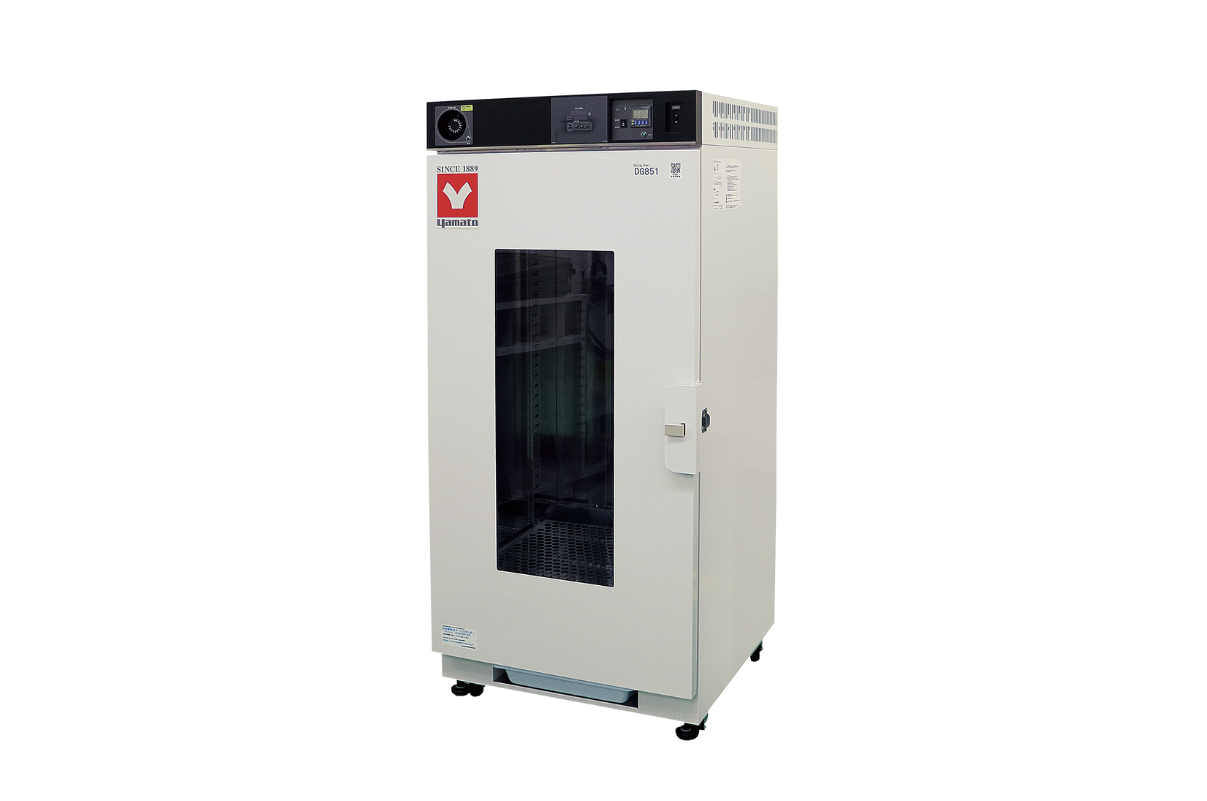

13.Drying Oven (Glassware Dryer)
A drying oven is a heated chamber used to remove water, moisture, and other solvents from objects. These ovens typically have a fan or turbine which sparks the convection process that heats and dries the materials inside.
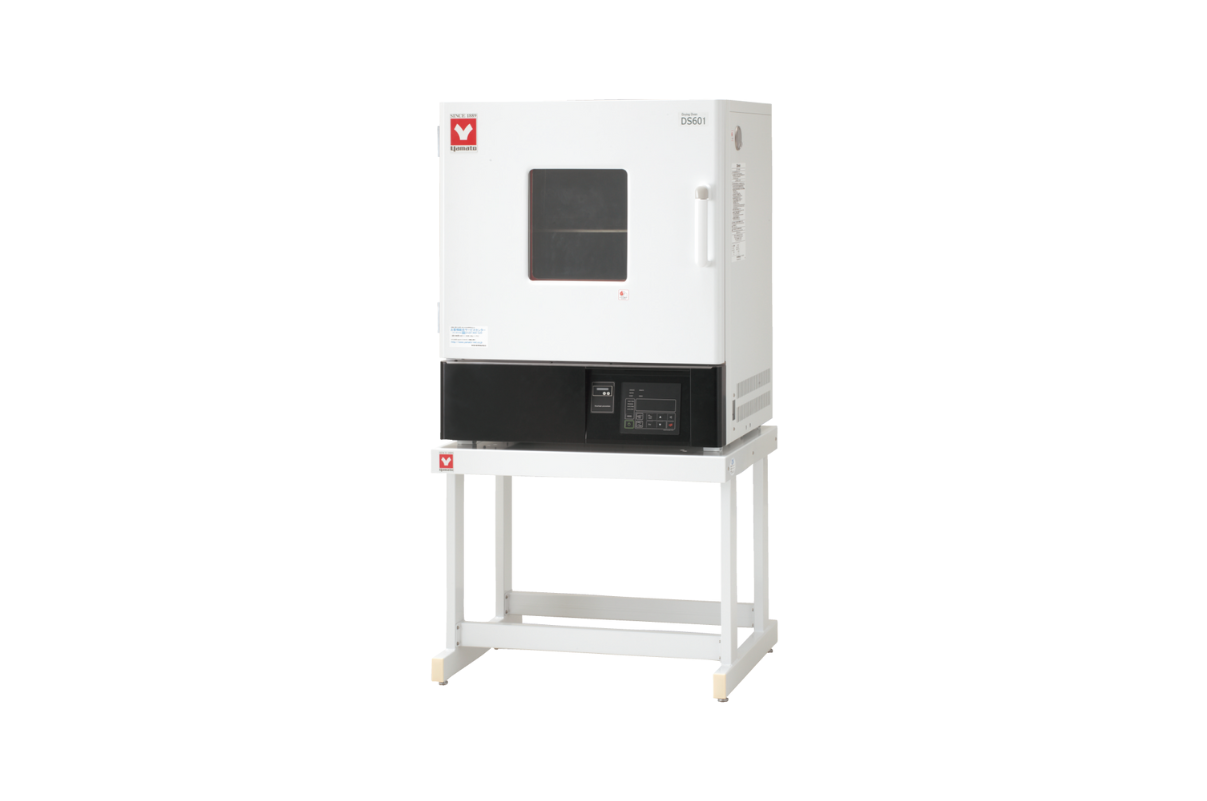

14.Programmable Drying Oven (Natural Convection)
A drying oven is a type of oven that is used to remove moisture from an object or material. The stove uses heat to evaporate the water, and the resulting vapor is vented outside. They are typically used for materials sensitive to water damage, such as electronic components or chemicals.
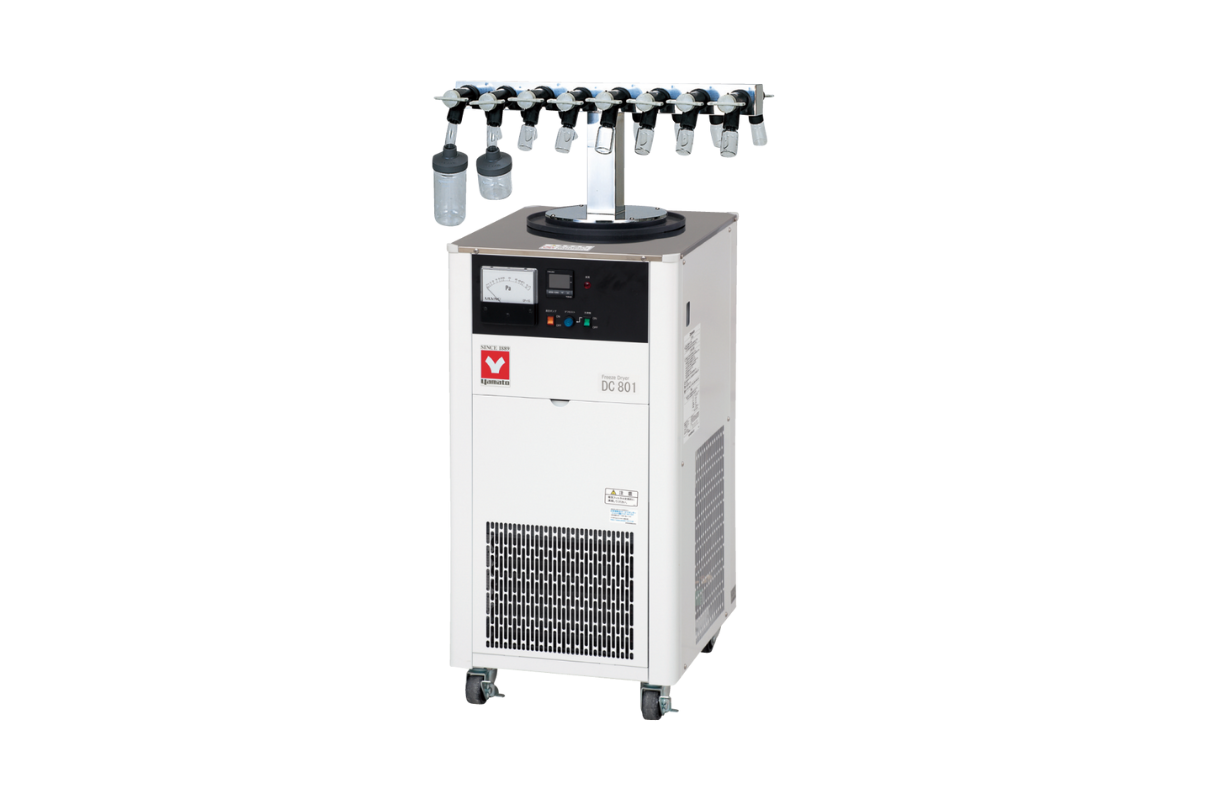

15.Freeze dryer- Lyophilizer
Lyophilizer and freeze dryer are synonymous names for the same equipment. A lyophilizer executes a water removal process typically used to preserve perishable materials, to extend shelf life or make the material more convenient for transport.
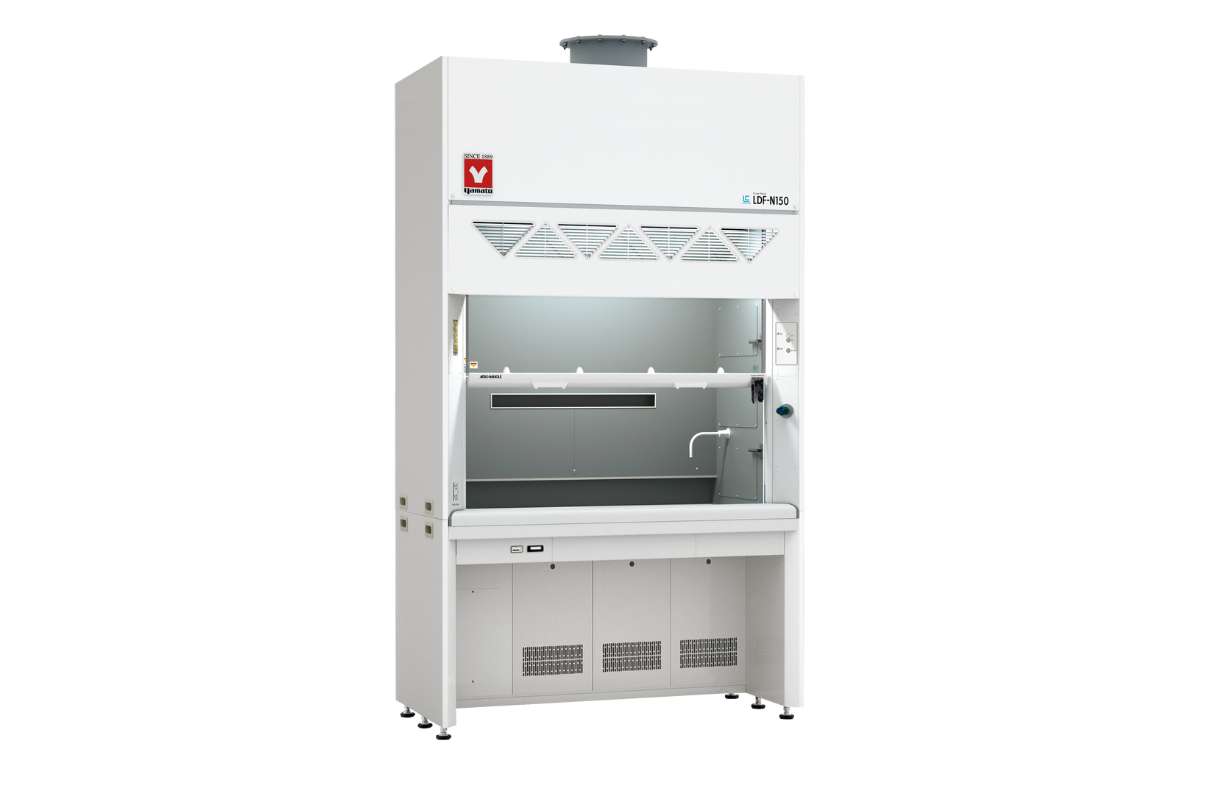

16.Fume hood
A chemical fume hood is a ventilated enclosure used to trap and exhaust vapors, gases, and nanoparticles. The exhaust fan is typically stationed at the top of the building and pulls air through the duct work connected to the hood and exhausts it into the atmosphere.
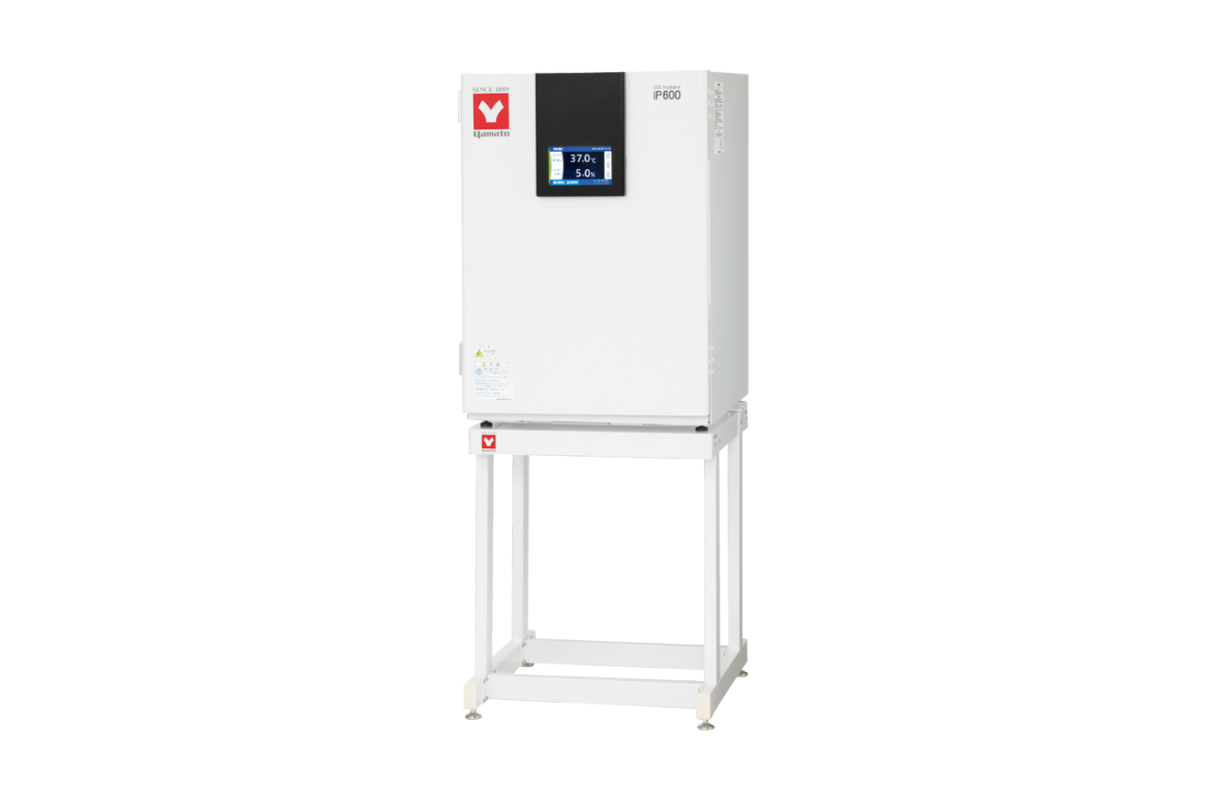

17.Incubator CO2
A CO2 incubator is a gassed incubator which creates a natural atmosphere in order to develop cell and tissue cultures. The temperature, humidity, and CO2 content must match the cell culture requirements.
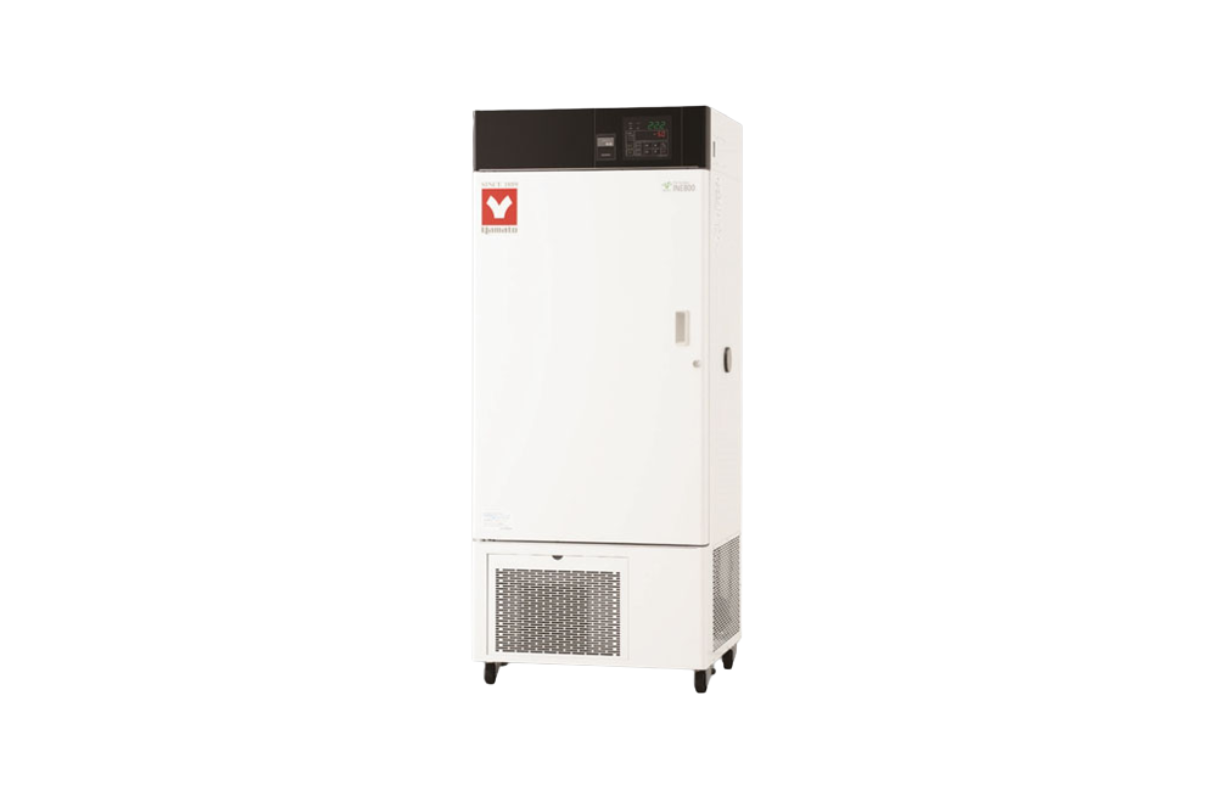

18. Incubator Low Temperature (Energy Saving & Programmable)
Refrigerated Incubator, also called low-temperature Incubator, are incubators that are designed to maintain temperatures below ambient to as low as about 10°C. These incubators keep the temperature at 20°C, necessary to perform a test called a Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD).
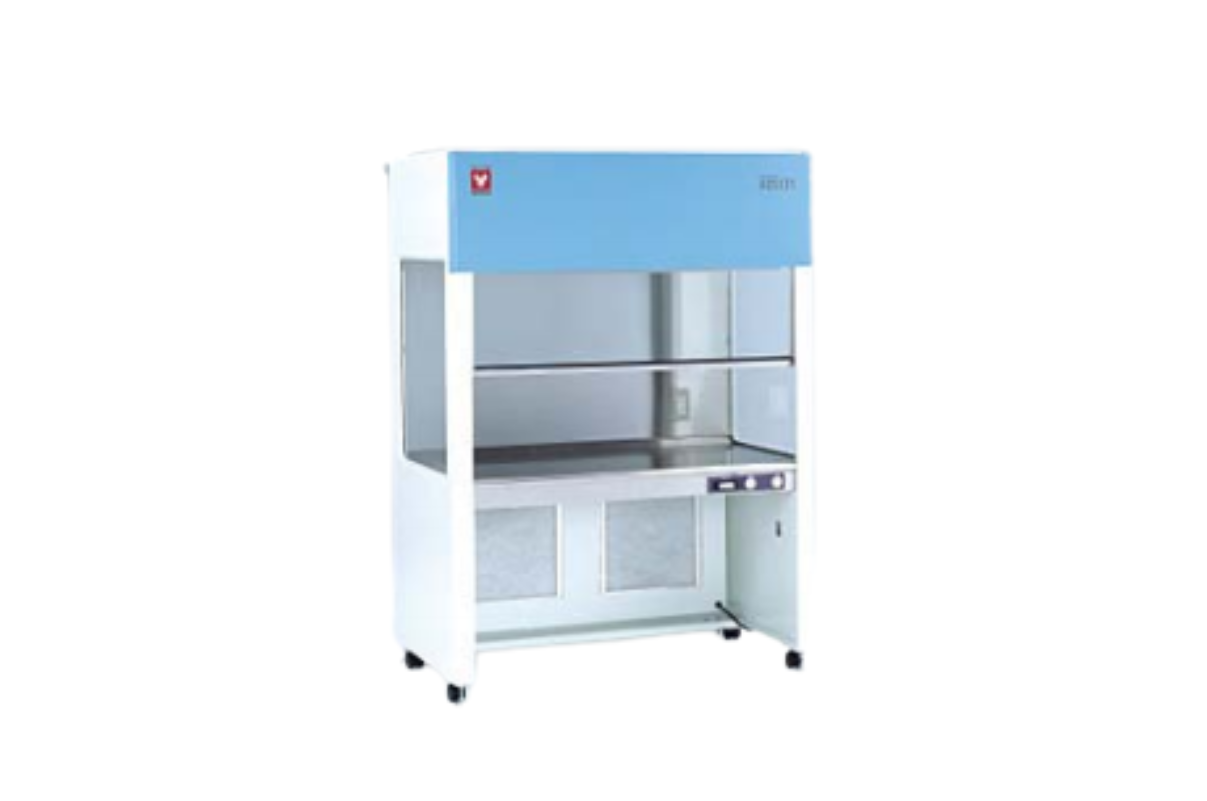

19. Laminar Airflow- Clean Benches, Biological
Laminar flow clean benches (also known as laminar flow hoods) provide an aseptic space to work with a product or specimen without contaminating it with particulates such as microorganisms. Laminar flow clean benches provide no protection for the user or the environment as airflow is directed out of the cabinet.
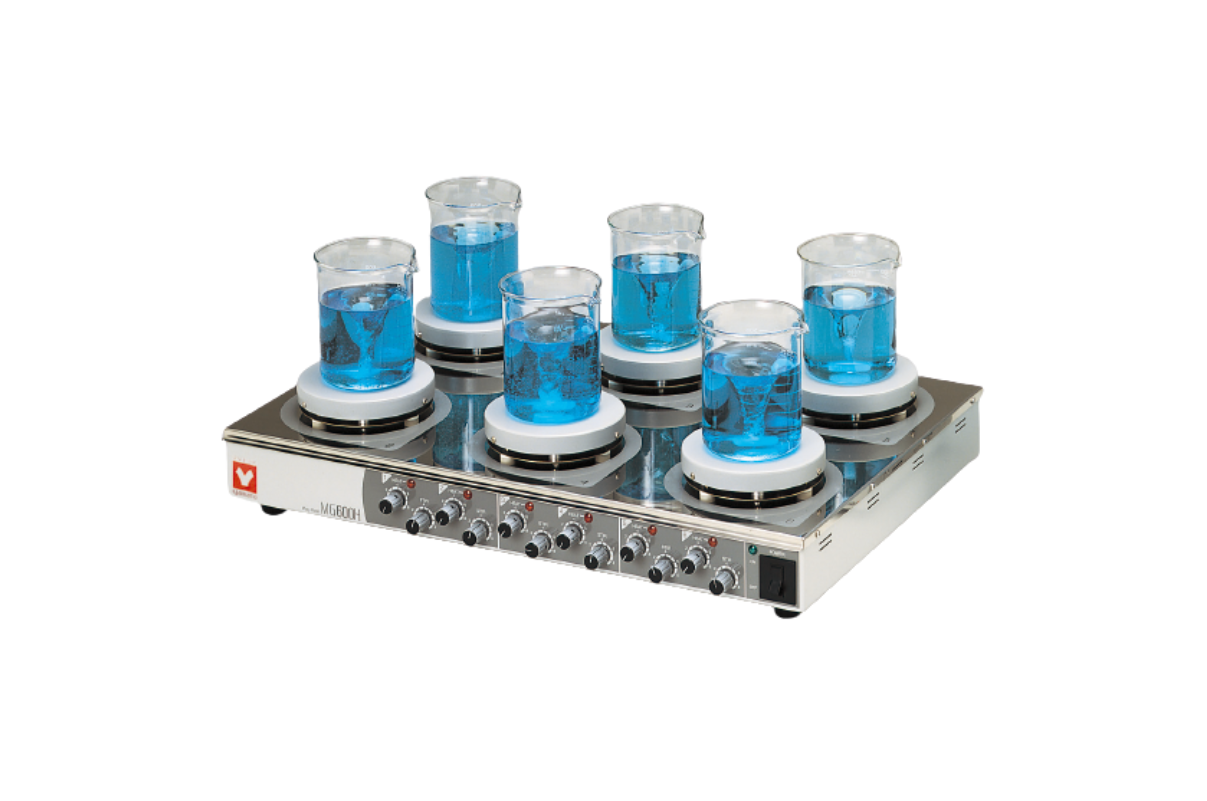

20.Magnetic stirrer with Hotplate and multiple pot
A hot plate stirrer or a hot plate magnetic stirrer is a laboratory instrument that is typically used to stir and heat the solution simultaneously. This helps the person performing the experiment speed up the reaction and properly dissolve the solute in the solvent.
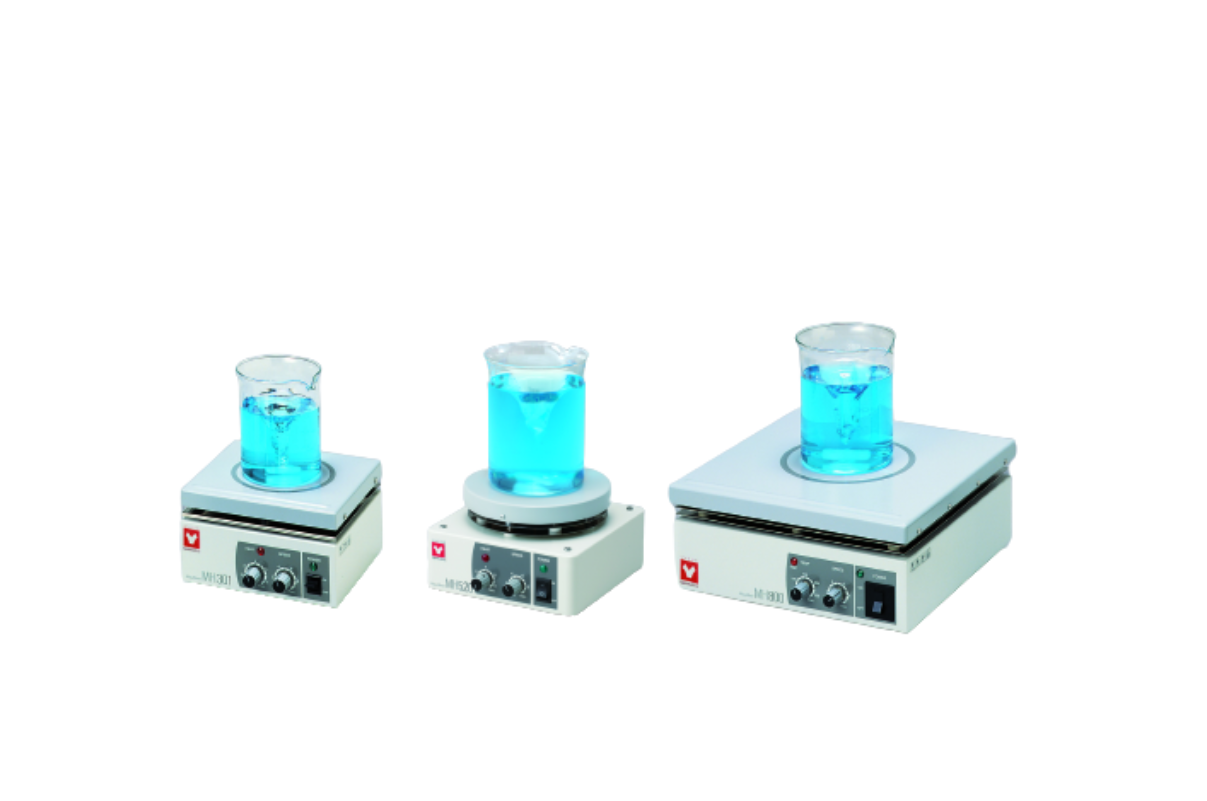

21.Magnetic stirrer with Hotplate single pot
The magnet is placed within a container and made to spin with an external magnetic field. Typically, this is produced by a stir-plate, which has another magnet rotating underneath the container. The chief advantage of this setup is that you can stir the liquid without having something stick into the container.
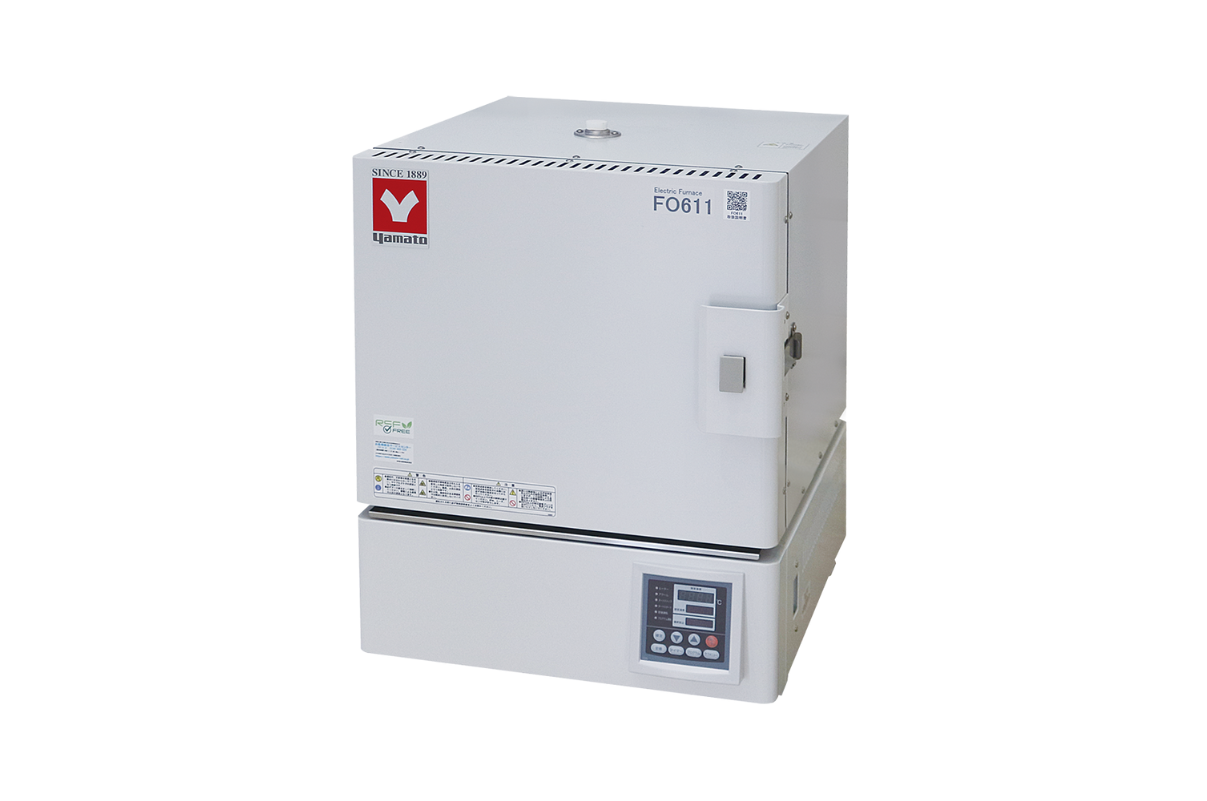

22.Muffle Furnace
A muffle furnace is a laboratory instrument used to heat materials to extremely high temperatures whilst isolating them from fuel and the byproducts of combustion from the heat source. Muffle furnaces allow for the isolation of a material to reduce the risks of cross-contamination and identify specific properties.
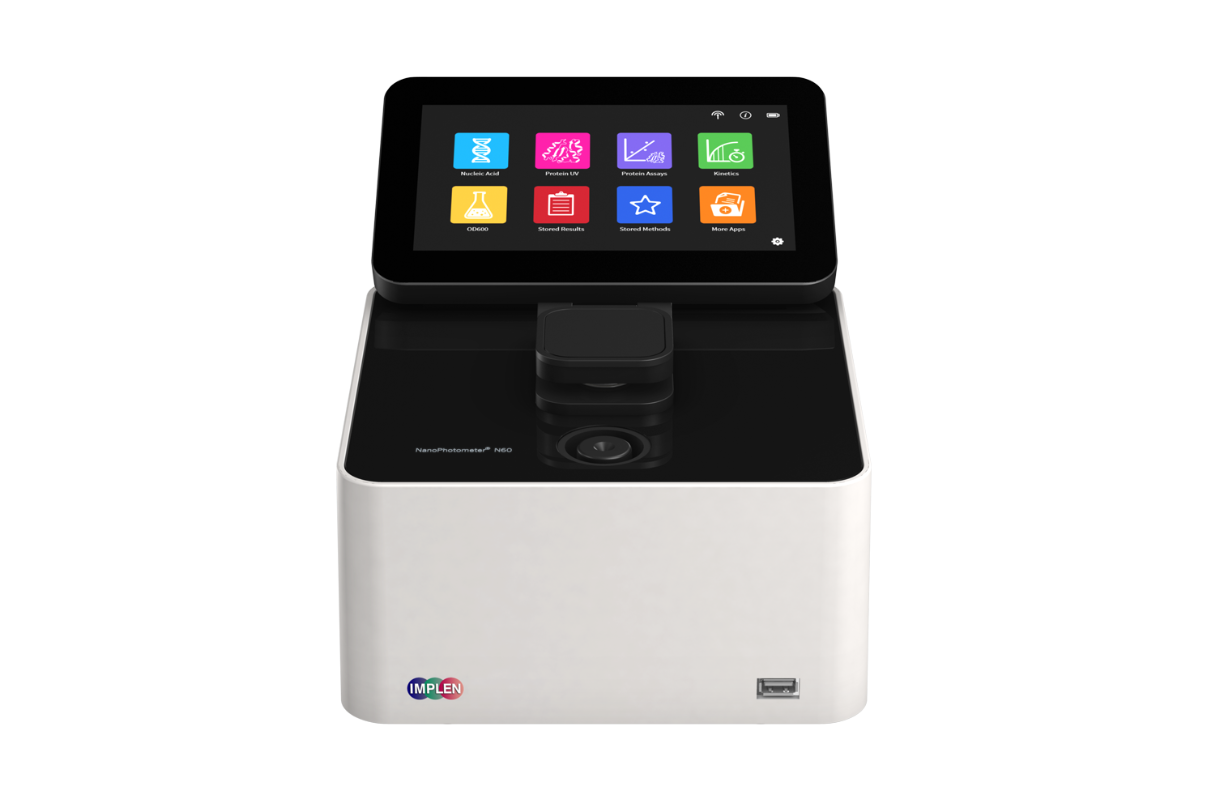

23.Nanodrop Spectrophotometer- Photo Absorbance Meter
NanoDrop spectrophotometers work on the principle of ultraviolet-visible spectrum (UV-Vis) absorbance. Nucleic acids absorb light with a peak at 260 nm. Purified proteins absorb light at a peak of 280 nm, while peptides and proteins that lack tryptophan and tyrosine residues absorb at a peak of 205 nm.
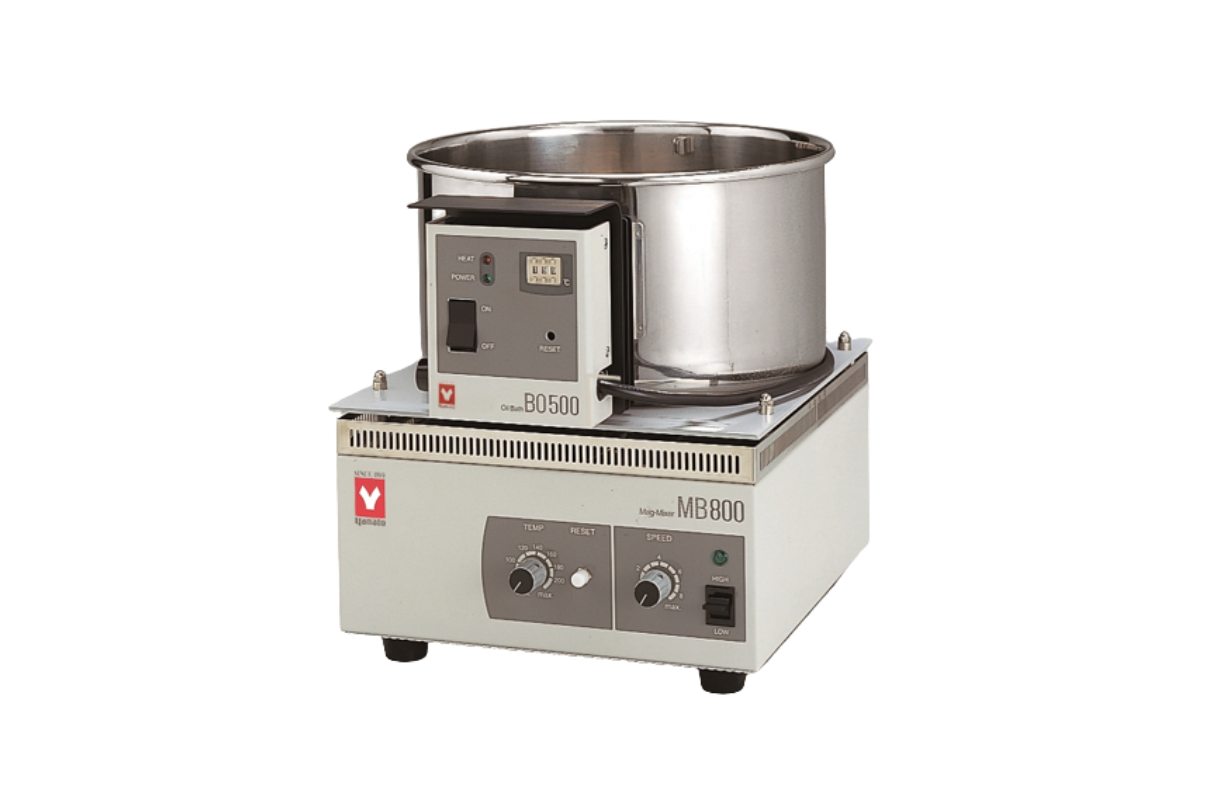

24.Oil Bath Economical
Oil baths are commonly used in synthesis to provide a very even and steady source of heat that is important for thermodynamic and kinetic control of many reactions. However, oil baths can also pose a potential for serious fire and injury risk in research laboratories, particularly when used improperly or neglected.
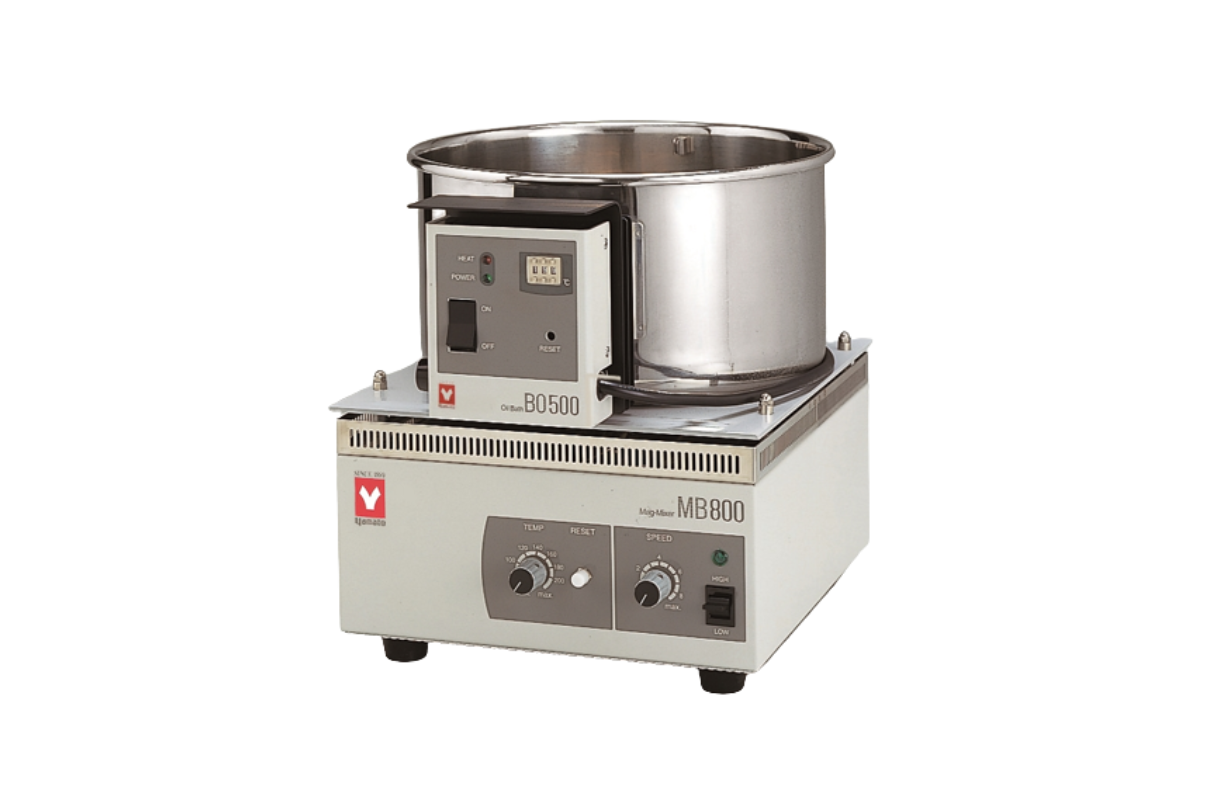

25.Oil bath with magnetic stirrer
An oil bath is a type of heated bath used for laboratories, it is the most common for heating chemical reactions. It is most commonly used in research laboratories for reactions that require heating temperatures up to 200 degrees Celsius. Oil baths provide more uniform heat compared to other heaters.
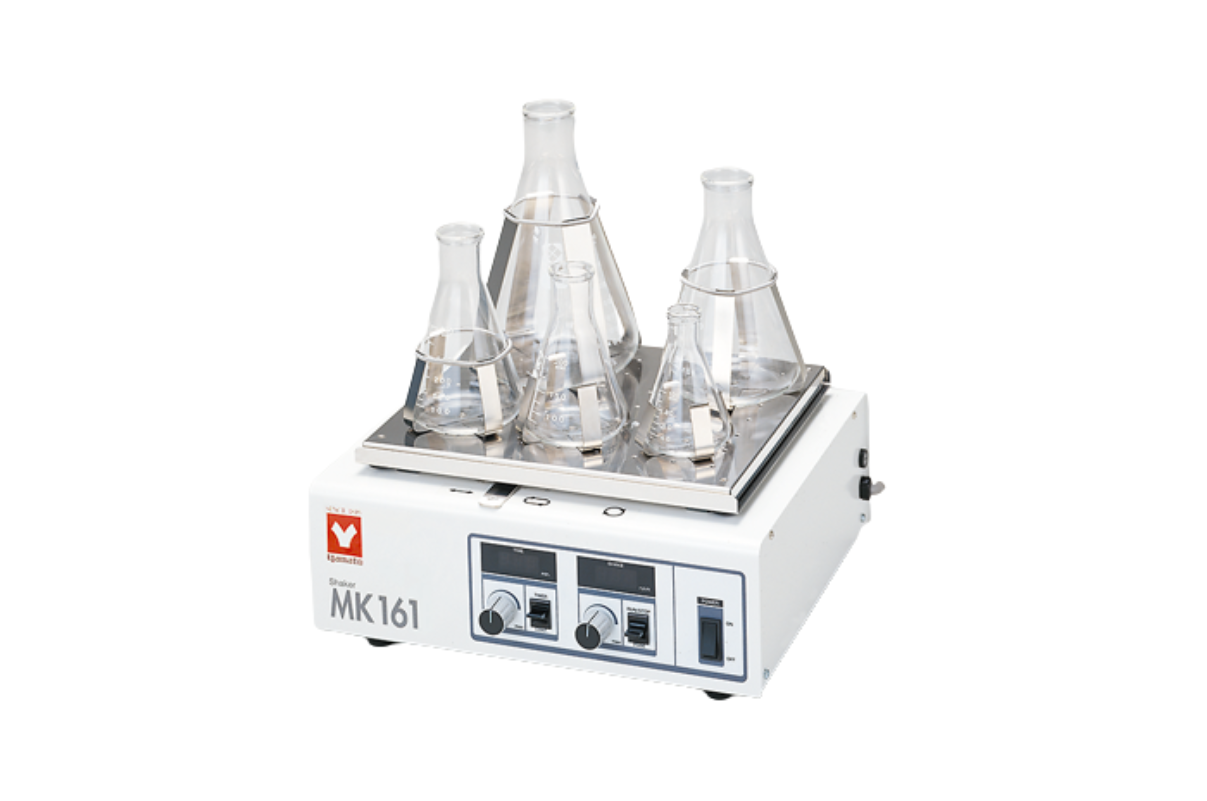

26.Shaker- Horizontal
The principle behind a laboratory incubator shaker is simple: it provides a controlled environment for samples to grow and develop while also providing mechanical agitation to mimic the natural movement of cells in their environment.

27. Shaker- Orbital
An orbital shaker is ideal for a variety of general-purpose shaking applications in cell culture, bacterial growth and suspension, staining and washing procedures. This type has a circular shaking motion with low to high speed with less vibrations, ideal for culturing microbes.
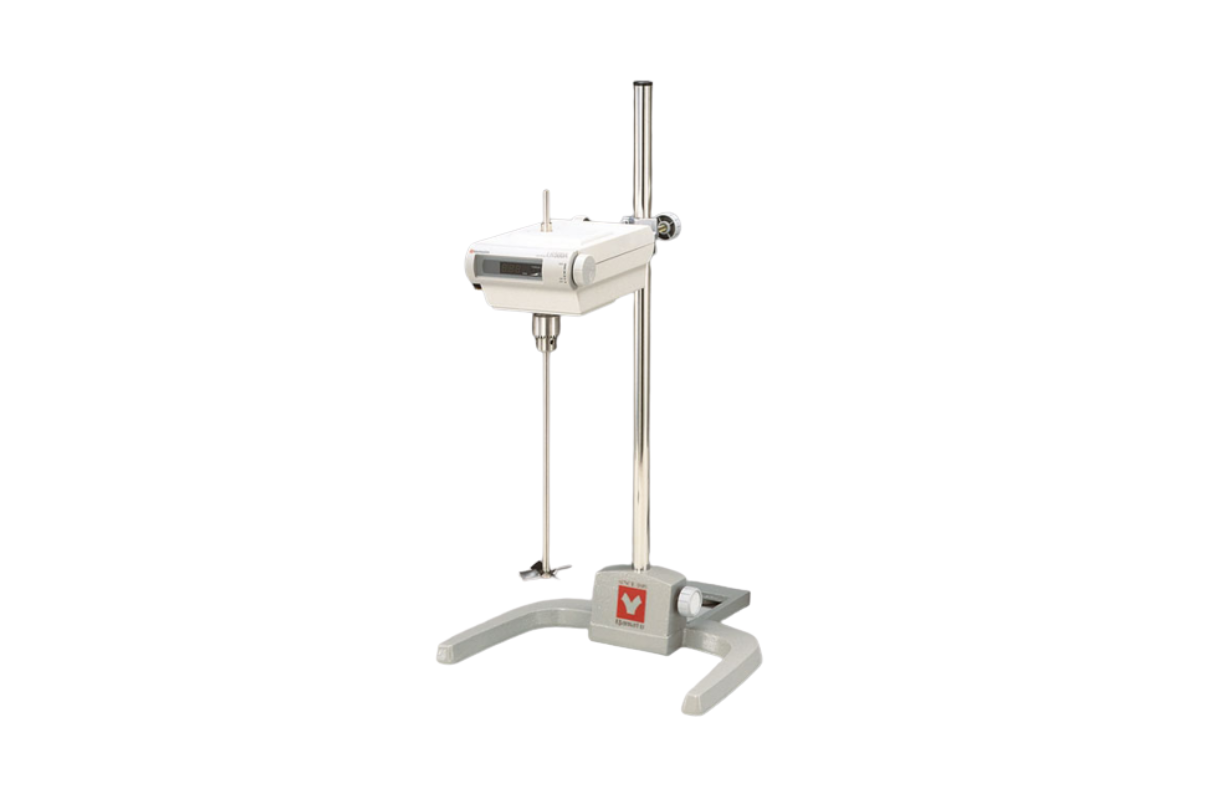

28. Stirrer (Laboratory) Vertical
A magnetic stirrer is a device widely used in laboratories and consists of a rotating magnet or a stationary electromagnet that creates a rotating magnetic field. This device is used to make a stir bar, immerse in a liquid, quickly spin, or stirring or mixing a solution, for example.
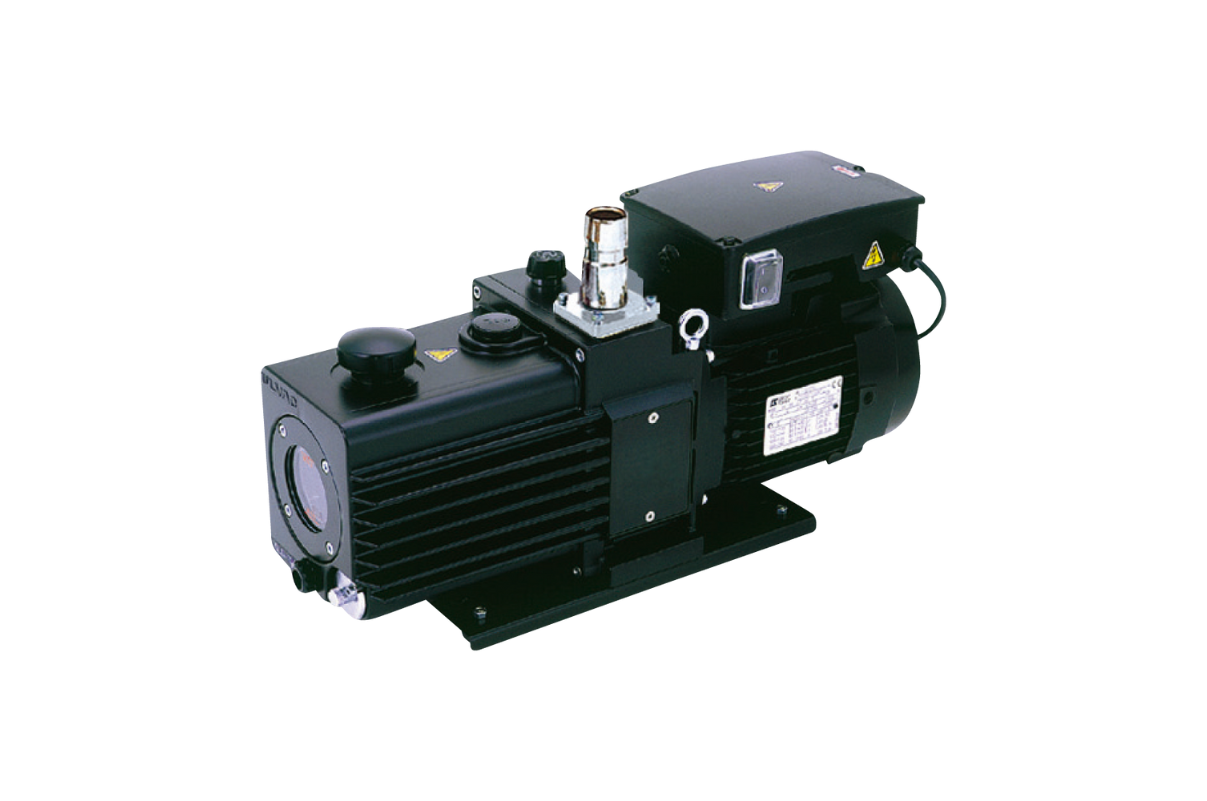

29. Vacuum pump High (oil, based, ultra-high): Vacuum Pumps, Compact
A full range of vibration-free and maintenance-free TiTan ion pumps, titanium sublimation pumps (TSP) and non-evaporable getter (NEG) pumps to achieve best ultimate pressures in the ultra-high vacuum.
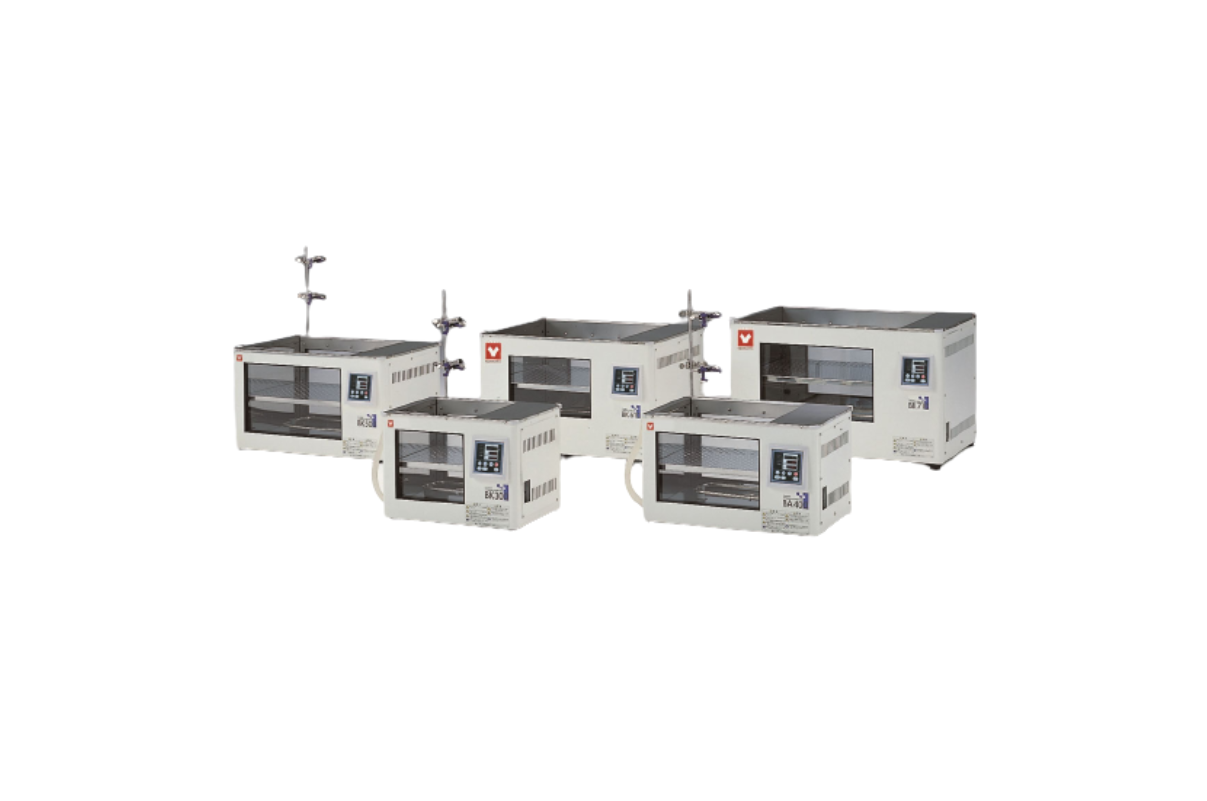

30. Water bath
A laboratory water bath is used to heat samples in the lab. Some applications include maintaining cell lines or heating flammable chemicals that might combust if exposed to open flame. A water bath generally consists of a heating unit, a stainless steel chamber that holds the water and samples, and a control interface.
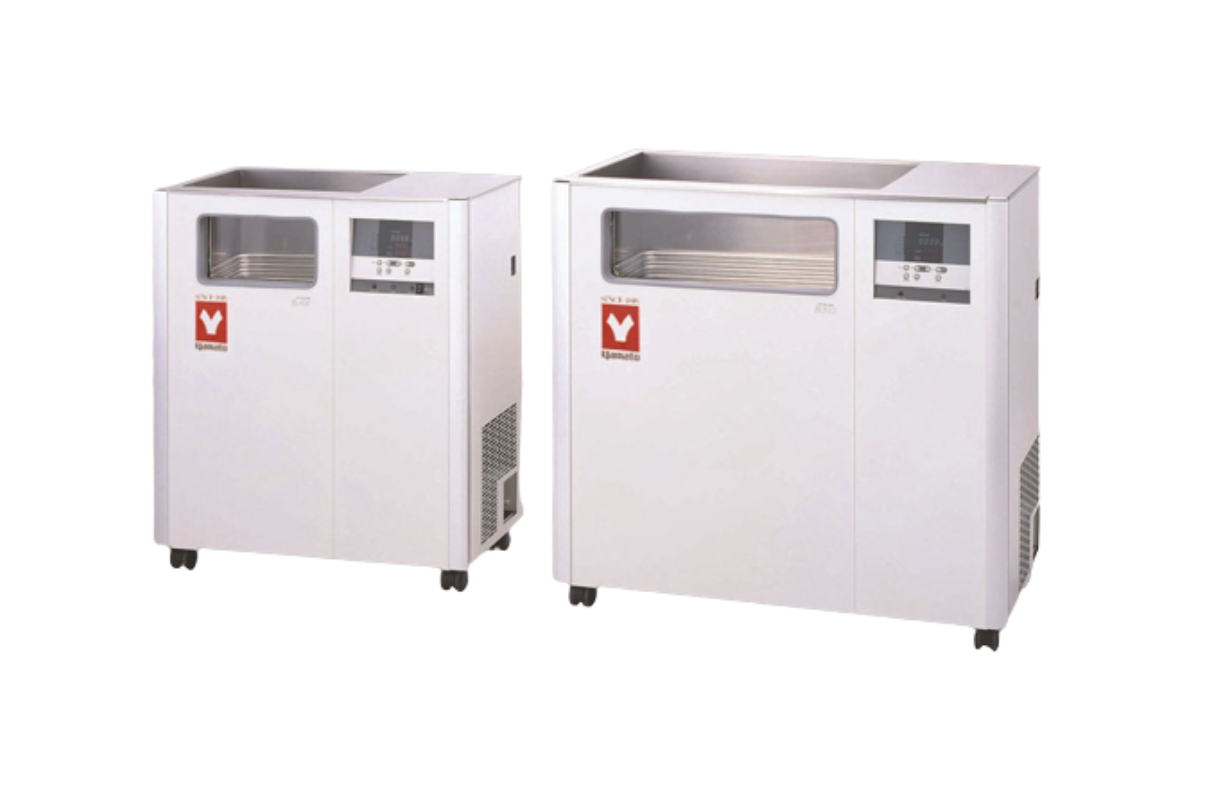

31.Water bath or Methanol bath with low temp. reaction
A water bath is a laboratory equipment that is used to incubate samples at a constant temperature over a long period of time. Water bath is a preferred heat source for heating flammable chemicals instead of an open flame to prevent ignition.

32. Water Purifier- Distilled water system/ Ion-exchange: ASTM D1193 Type 2 water
Water purifiers not only clean the water but also make it safe by removing bacteria that cause diseases such as cholera, typhoid, diarrhoea, and cancer. It may also help to prevent rectal and colon cancer, as unfiltered water has been linked to the development of these diseases.

33. Water Purifier- Ultrapure water for biological and chromatography applications (Resistivity >18Ω) ASTM D1193 Type-1
The first and the purest water is ultrapure water. It is designated as Type I by the ASTM standards. Among the four types of pure water, ultrapure water is the most desired water used in the laboratory. Many laboratory water purification systems have this feature of obtaining type I water easily.

34. Balance- Analytical, 4-digit, 1.0 mg accuracy
Analytical balances are used for very accurate, quantitative measurements of mass to the nearest 0.001 g. (Some read to 0.0001 g.) These are delicate instruments, subject to errors caused by vibration and drafts.

35. Balance- Electric, Top loading, 0-50Kg, LED, 1gm
Typically top-loading laboratory balances used to weigh quantities to a precise number; less precise, but with a higher capacity, than analytical balances, and may include draft/dust doors, auto-leveling, and rapid stabilization features.
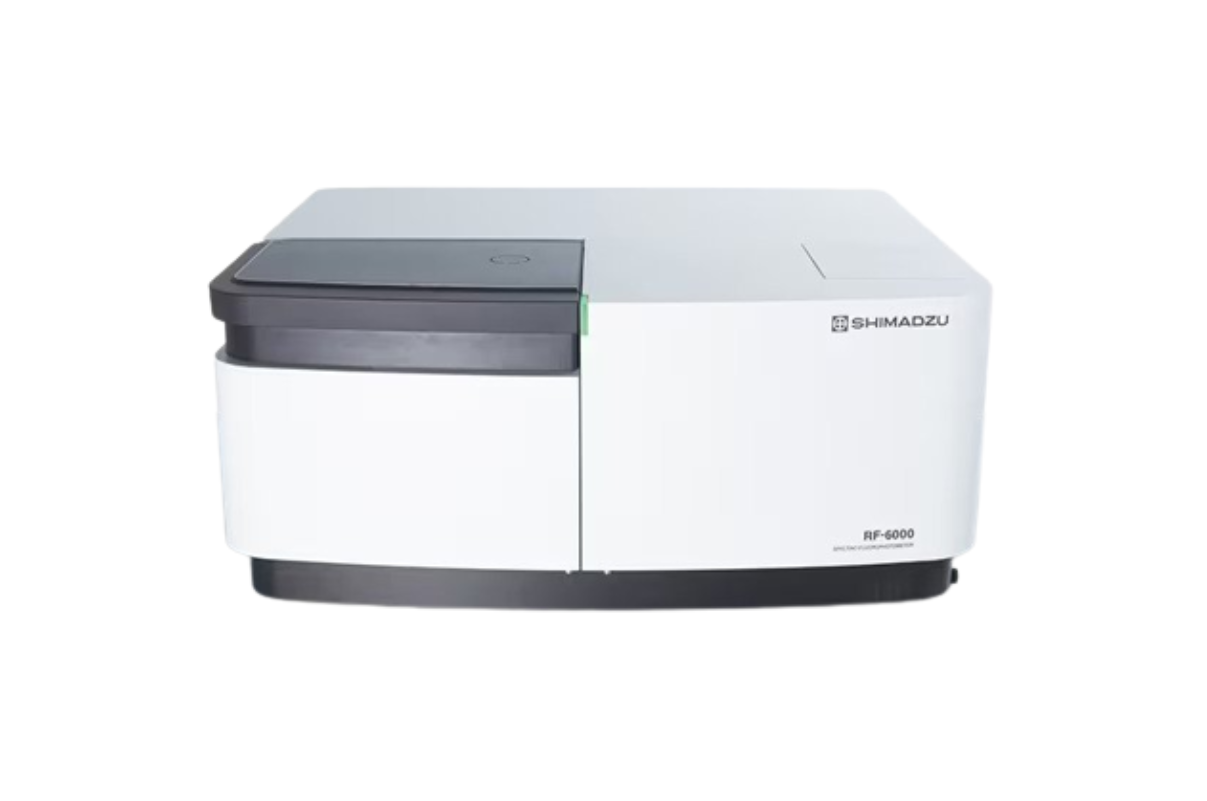

36. Fluorescence Spectrophotometer
Fluorescence spectroscopy is an investigative method based on the fluorescence properties of the sample under study, and is used for quantitative measurements of chemical products. Fluorescence spectroscopy analyzes fluorescence from a molecule based on its fluorescent properties.

37. GC-MS/MS, Triple Quadrupole with EI, CI, NCI, NIST Library, and Method Package
Solutions for Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) Wiley Spectral Libraries help researchers to positively identify trace metabolites and compounds during routine toxicology screens, crime scene analysis, or medical research.
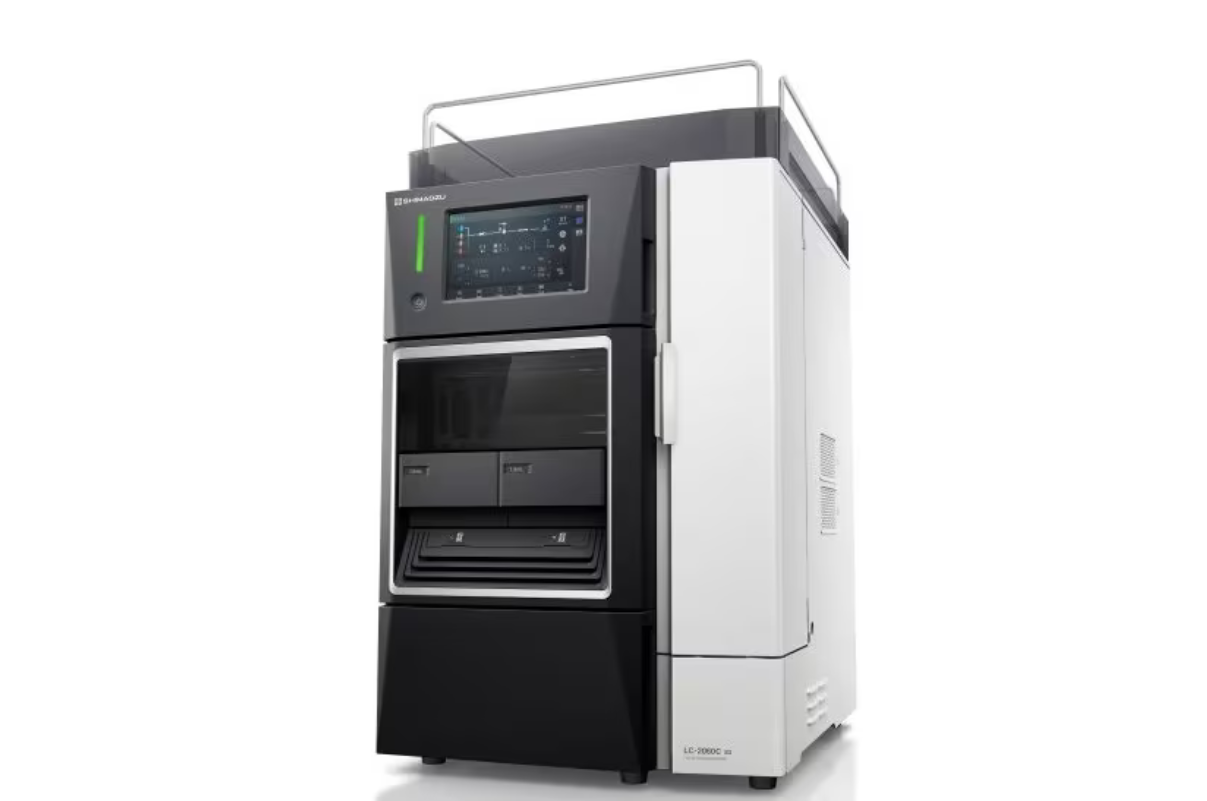

38. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with PDA and Fluorescence Detector
A common type of detector in HPLC is the photodiode array (PDA) detector, sometimes called a diode array detector (DAD). With a PDA detector, researchers can gather information about the sample separations' identity, quantity, and purity as they exit the HPLC column.
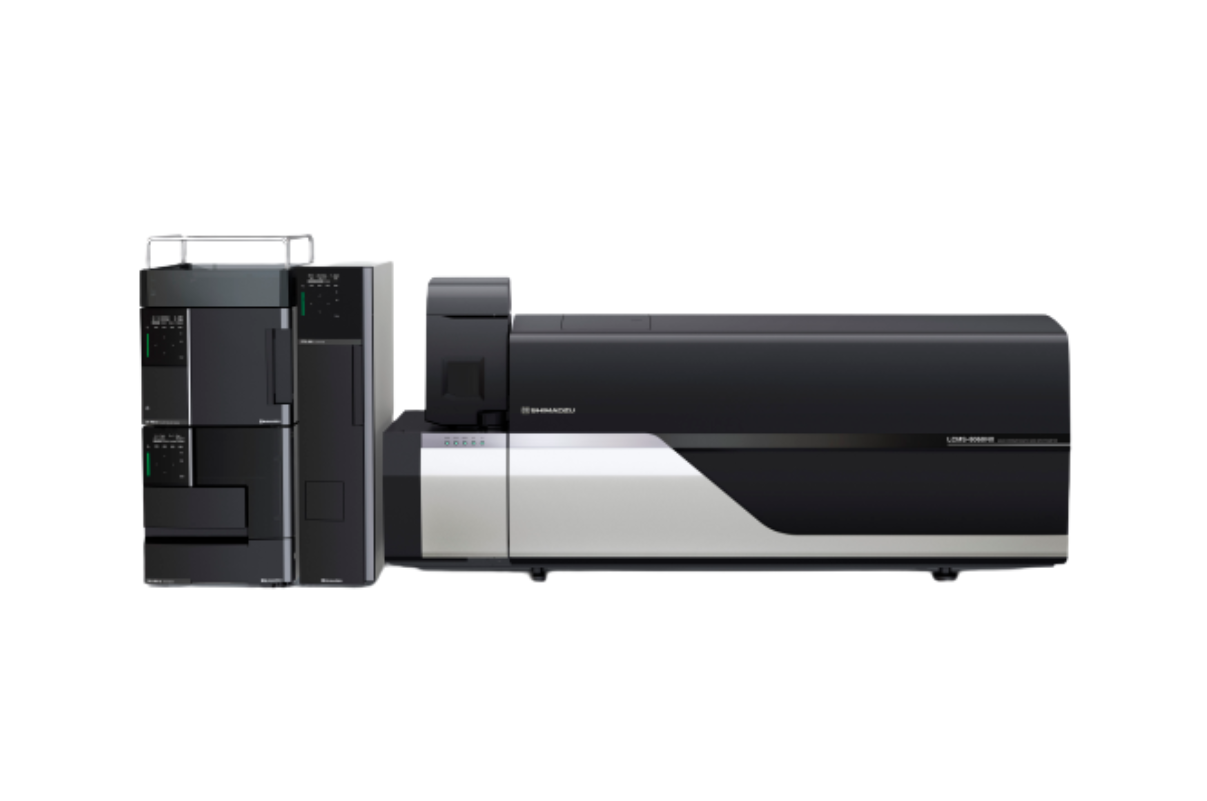

39. LC-MS/MS Triple Quadrupole with ESI, APC, Pesticide Primary Metabolites, and Fatty acid Method Package
Liquid Chromatography Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) can be used for a wide variety of applications. The applications include identification confirmation of organic chemical compounds, chemical residue analysis, and trace level contamination or adulteration detection and quantitation.
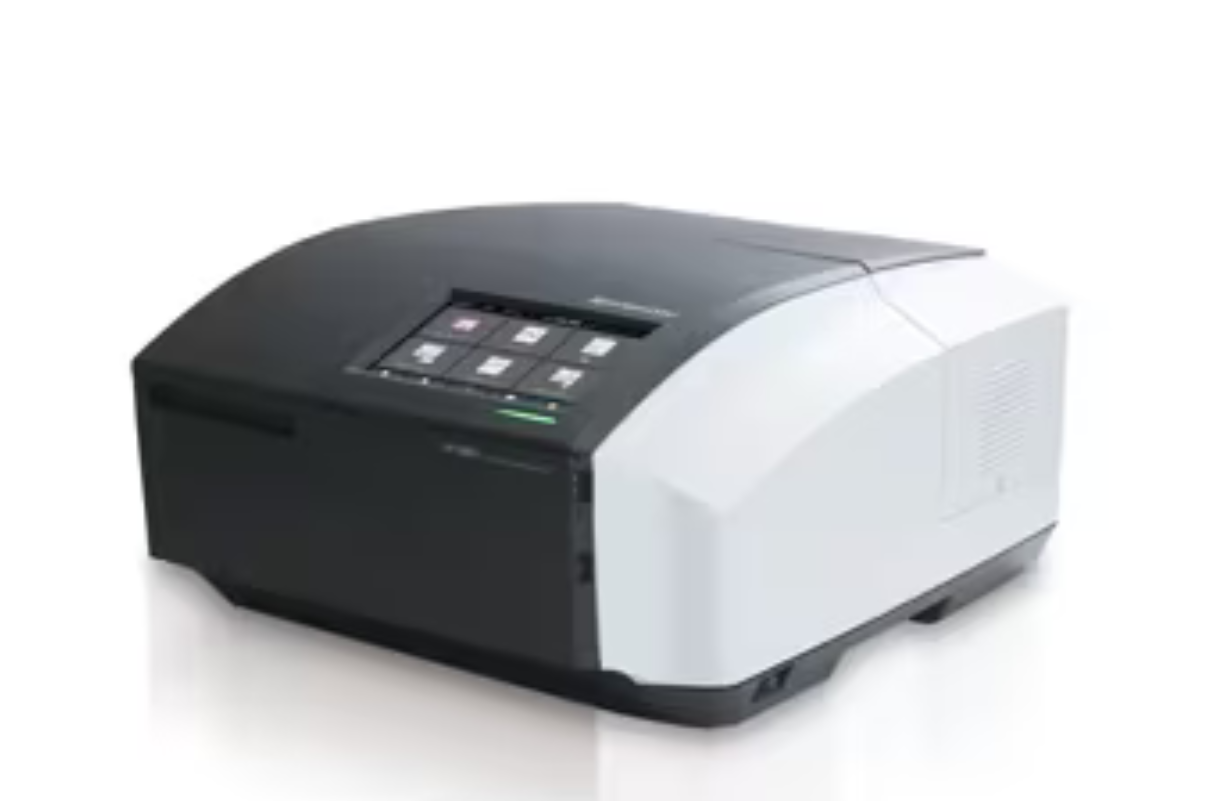

40. UV-VIS. Spectrophotometer
UV-Vis spectrophotometers provide fast and efficient analysis, allowing researchers to obtain results within a few seconds. It is used to quantify nucleic acid and protein content in biological samples and for quality control in drugs and food industries.
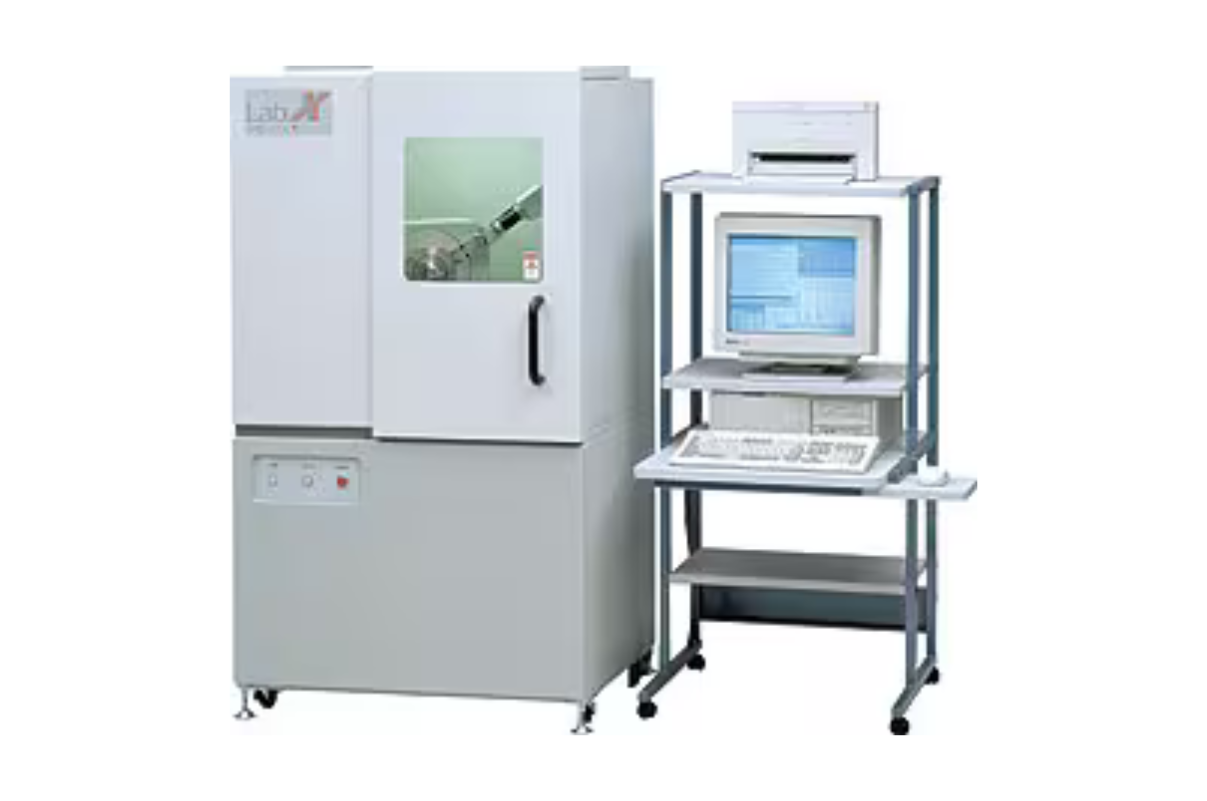

41. X-Ray Diffractometer, Powder (P-XRD)
The XRD-6100 offers solutions encompassing wide-ranging analysis requirements, from routine qualitative and quantitative analysis to state change analysis, including stress analysis, residual austenite quantitation, crystallite size/lattice strain, crystallinity calculation, materials analysis via overlaid X-ray .
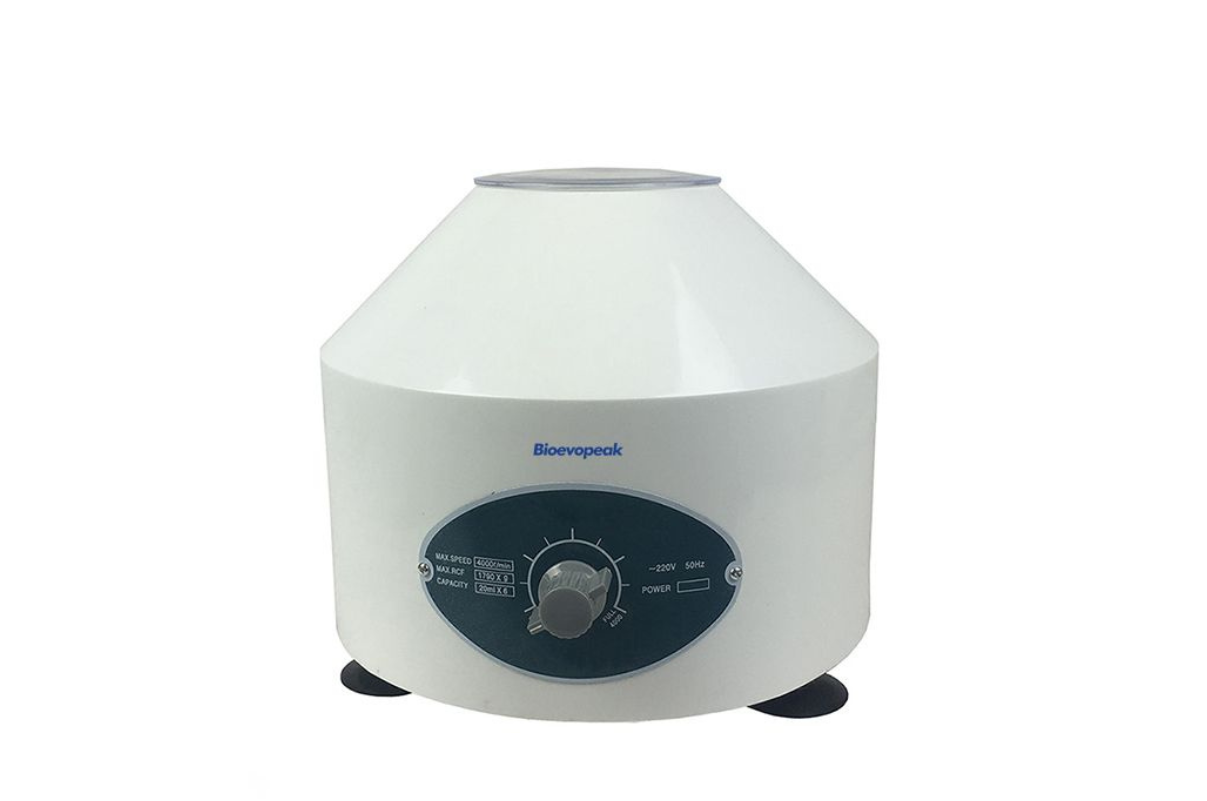

42. Centrifuge Low speed, Economical Type
Centrifugation is the first step in most fractionations. Through low-speed centrifugation, cell debris may be removed, leaving a supernatant preserving the contents of the cell. Repeated centrifugation at progressively higher speeds will fractionate homogenates of cells into their components.
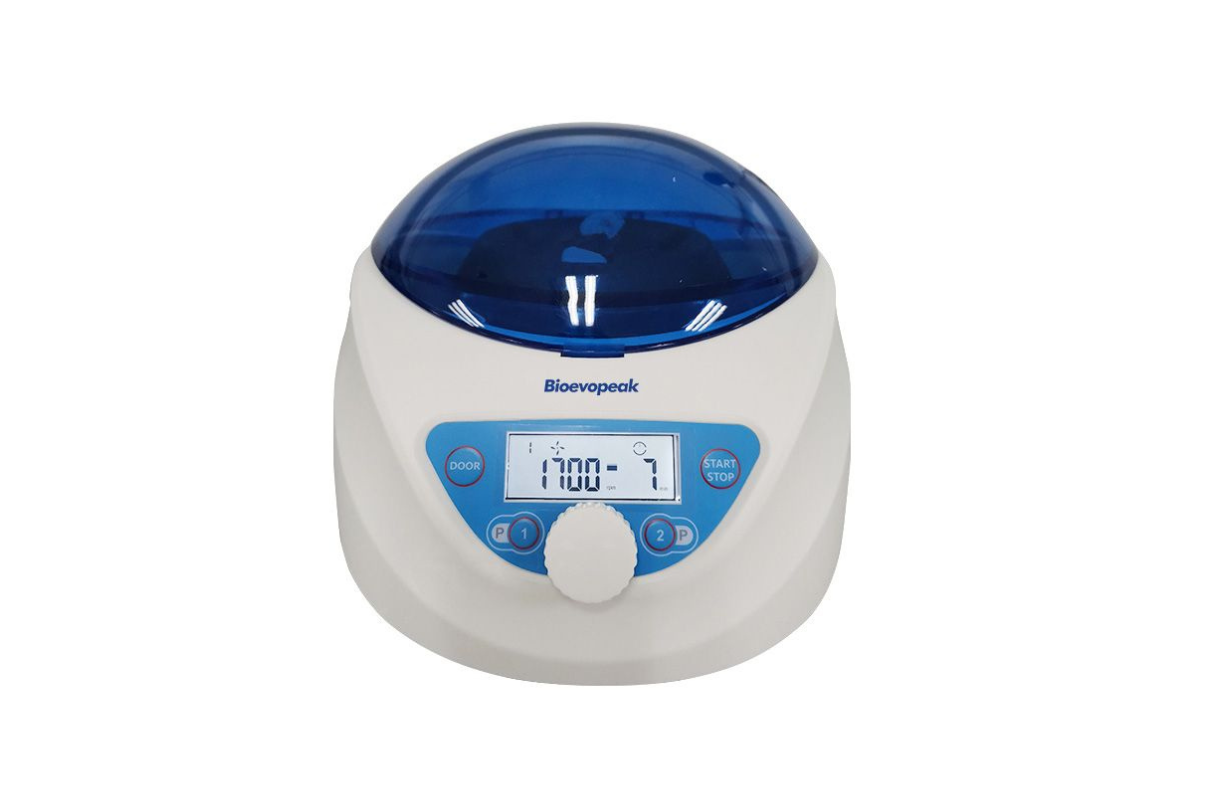

43. Centrifuge, Micro Low Speed
The centrifuge is ideal for general laboratory applications including biological sample separations of cellular materials, blood, urine, sperm etc. As well as clinical applications including PRP, PRF, lipid cell separation and stem cell isolation.
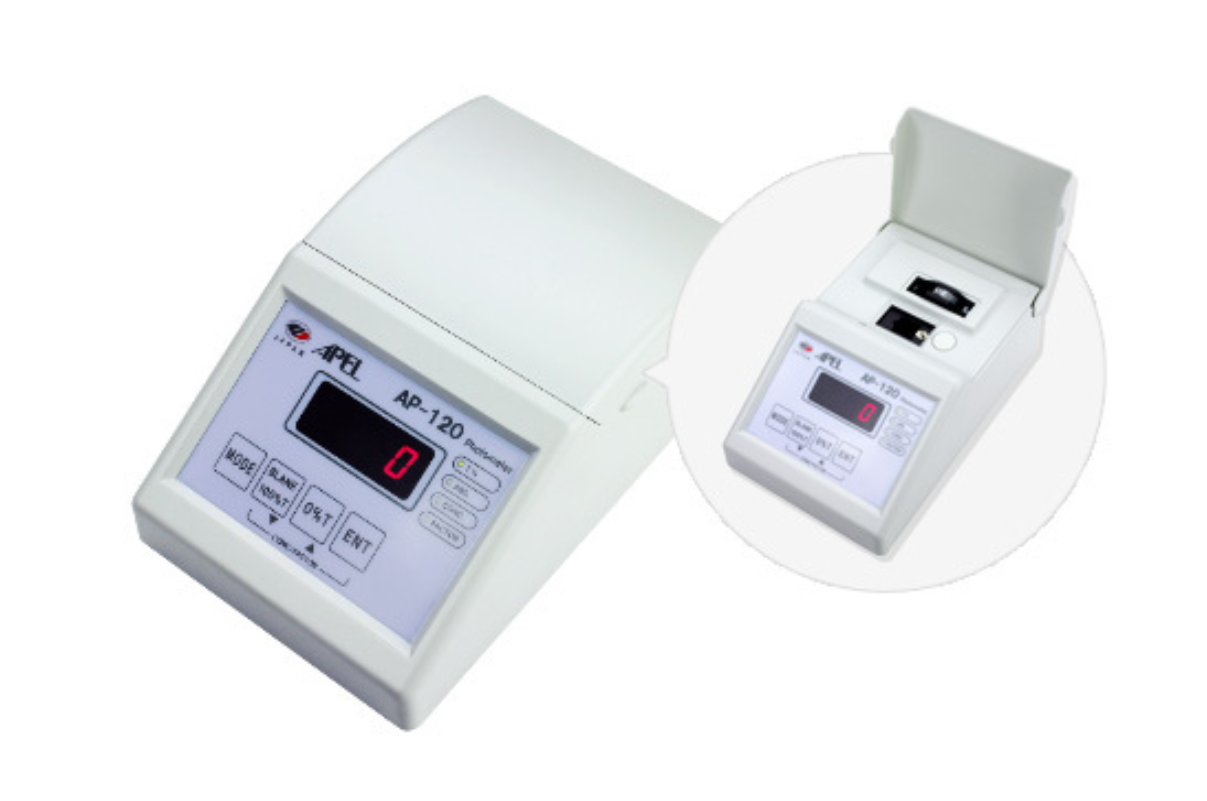

44. Colorimeter Portable Intelligent
The portable colorimeter can be used in clinical laboratories and hospitals to measure different biochemical components in a range of biological samples, such as blood, plasma, serum, CSF, urine, and other body fluids.
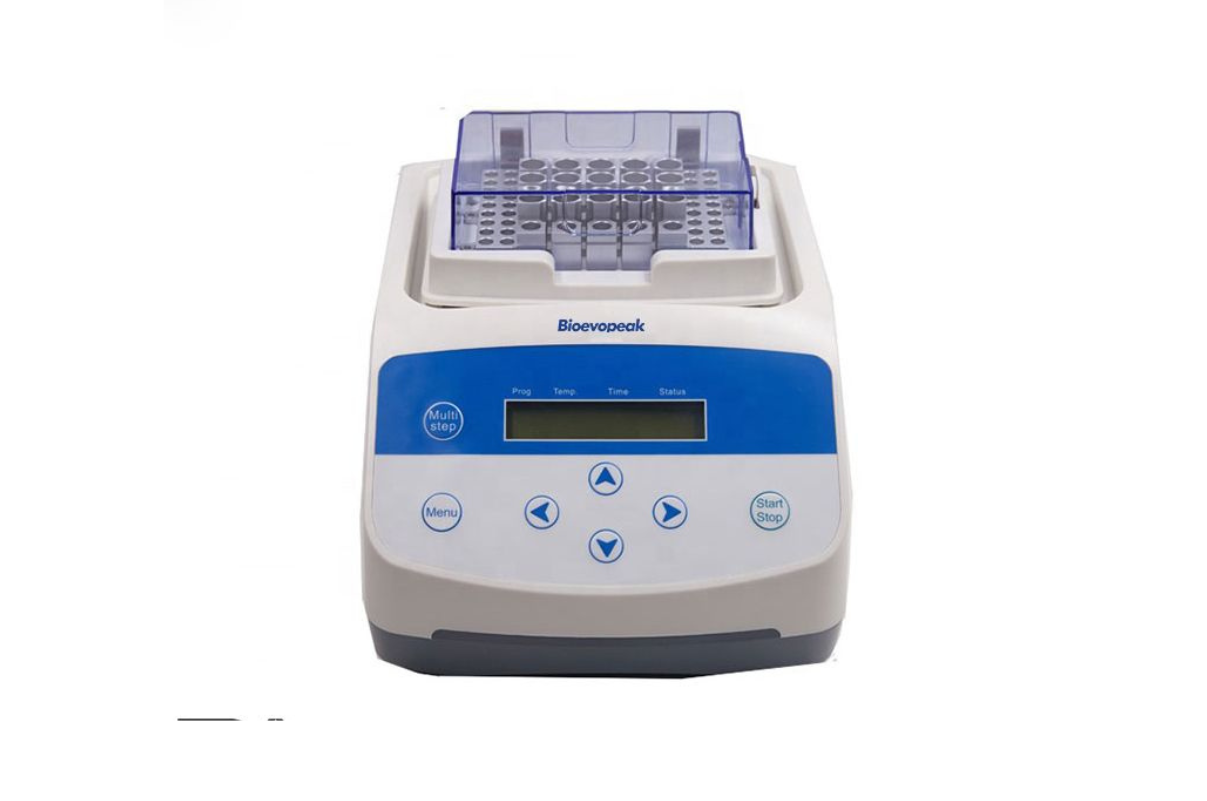
45. Dry Bath Incubator (5℃-100℃)
Dry bath incubators are used in laboratories to heat samples prior to a variety of applications and are used widely in molecular, microbiological, and biochemistry labs. The term dry bath is used to differentiate these types of incubators from other methods of heating that rely on using a liquid.
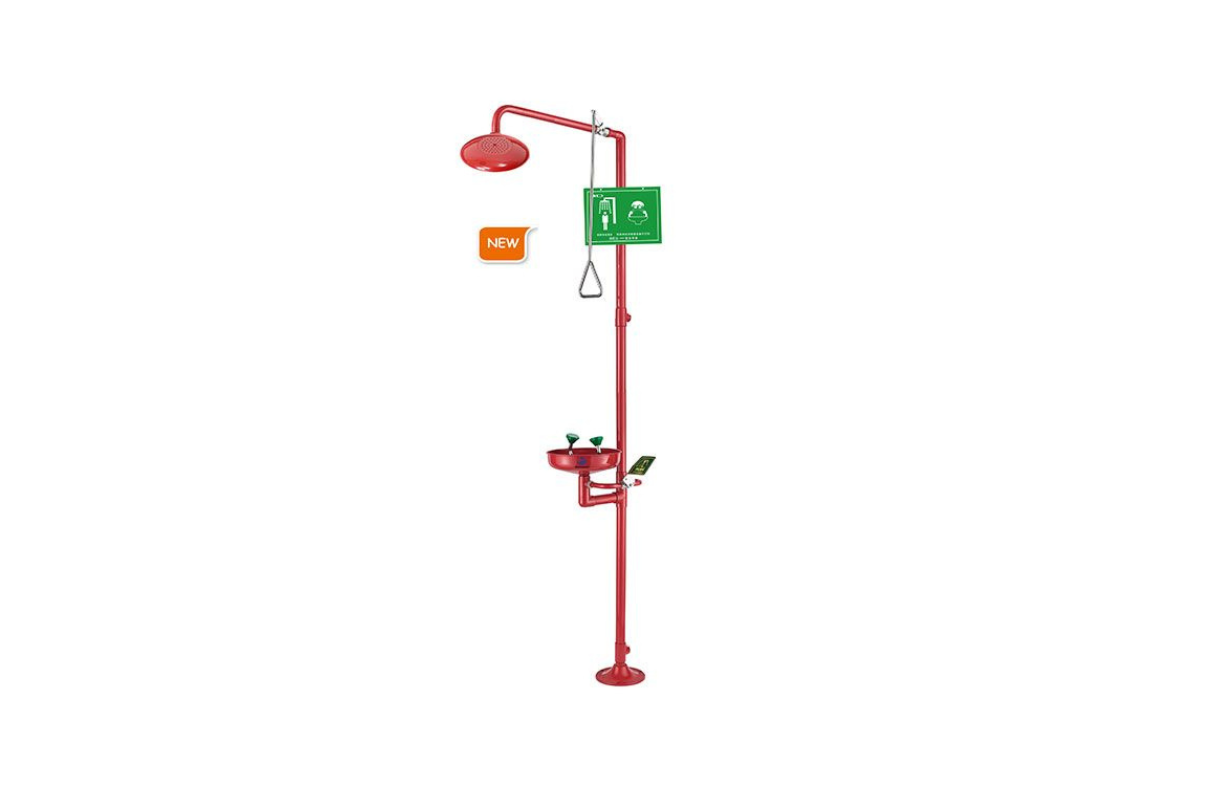
46. Eye-Face wash and shower combination station
Combination eye wash stations combine a shower and an eye wash in a single unit. The shower provides a full body washdown to prevent injury after being exposed to hazardous materials. The eye wash flushes irritants from eyes to treat and prevent eye injuries.

47. Freezer -86 ℃ Ultra Low Temperature
An ultra low temperature (ULT) freezer is a refrigerator that stores contents at −40 to −86 °C (−40 to −123 °F). An ultra low temperature freezer is commonly referred to as a "minus 80 freezer" or a "negative 80 freezer", referring to the most common temperature standard.

48. Homogenizer High Speed
Aside from mixing, homogenizers are used for emulsifying, suspending, grinding, dispersing, and dissolving. The pharmaceutical, beverage, and chemical industries rely on homogenizers for the production and quality of their products.

49. Ice Maker
Ice flakes and cubes are very important for maintaining the conditions of proteins, enzymes and other reagents during lab experiments, for a transit time outside refrigerator and deep freezers. This Follet ice machine makes rapidly makes ice and keeps it un-melted for a long time.

50. Incubator Constant Temperature Shaking (Benchtop)
The constant temperature incubator shaker is a small desktop shaking incubator that combines the functions of air bath constant temperature and horizontal shaking. It is widely used in biotechnology, microorganisms, medical analysis and other fields.
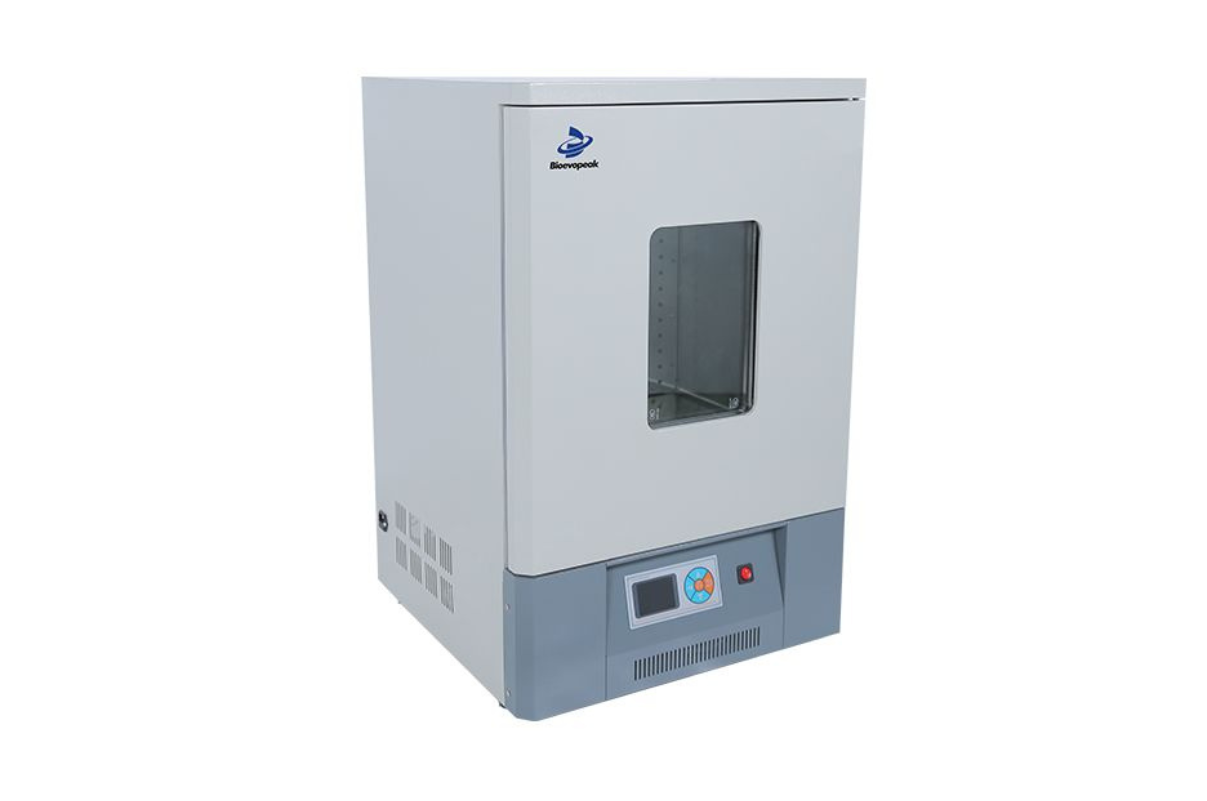

51. Cooling Biochemical Incubator
Biochemical Incubator CBI is the most widely used cooling incubator in environmental protection department, health and epidemic prevention department, agricultural department institute. Biochemical Incubator CBI is widely used in water analysis, BOD determination, microbial culture and breeding experiment.
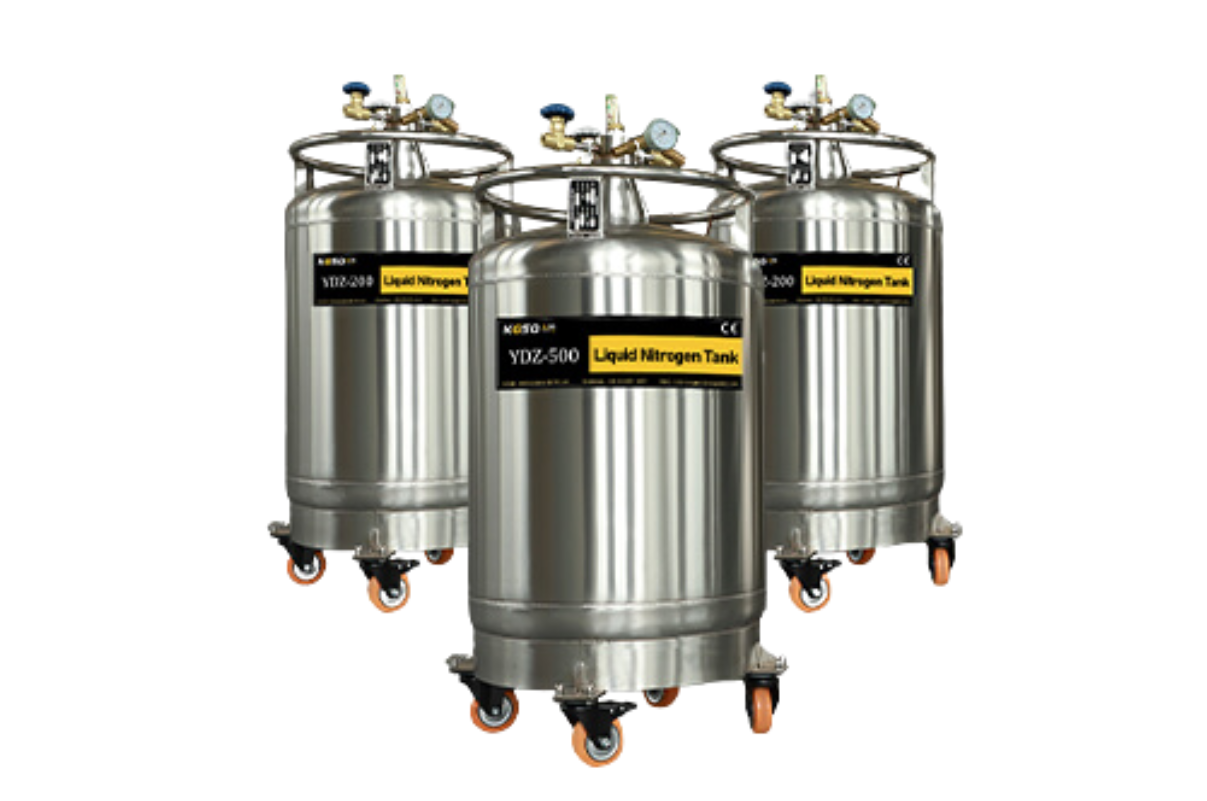

52. Liquid Nitrogen Storage Tank
Liquid nitrogen is used for a wide range of applications from medical and scientific research to food and beverage. LN2 is frequently used in medical and scientific research as it can be used to freeze tissue samples, freeze blood products, and preserve biological specimens.
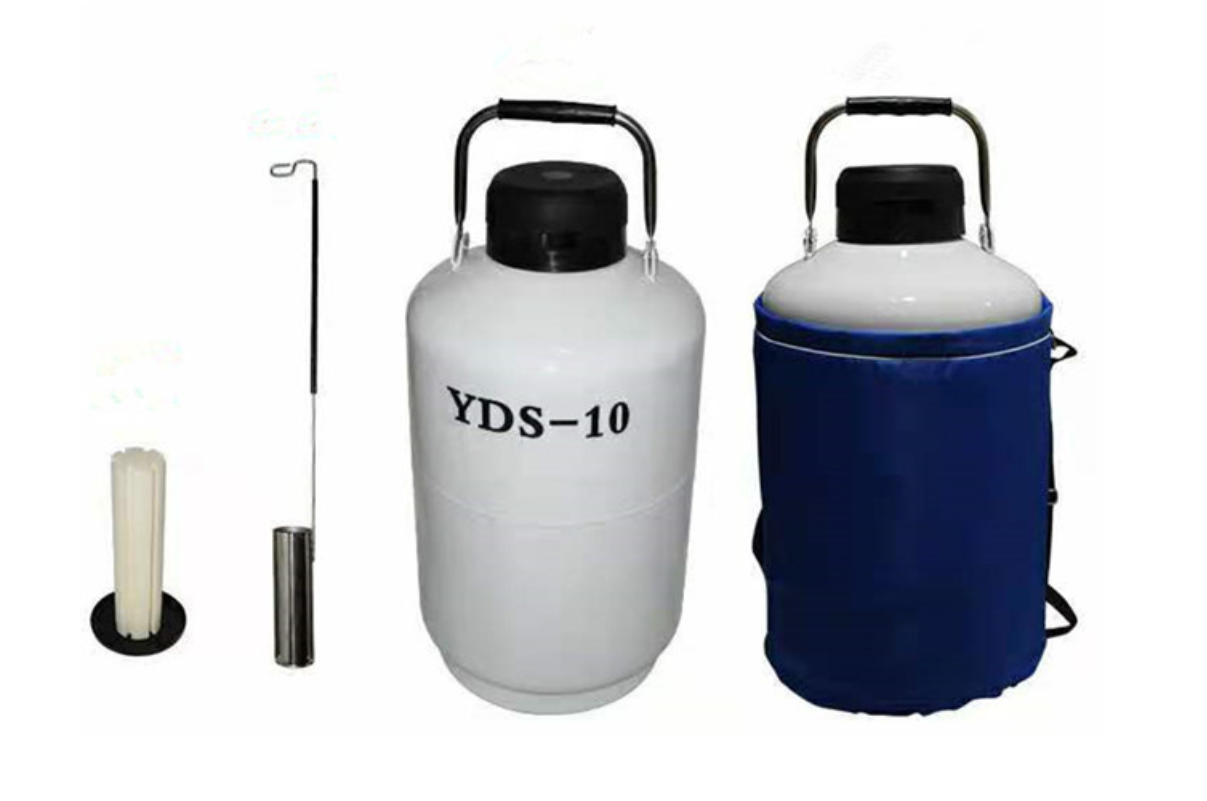

53. Liquid Nitrogen Vessel Transport Type
A dewar is an insulated container used for storing cryogens. Most dewars are double-walled and vacuum-insulated; some also use an insulated packing material in the vacuum jacket. Dewars used for temporary storage of cryogens may be constructed of foam insulation.
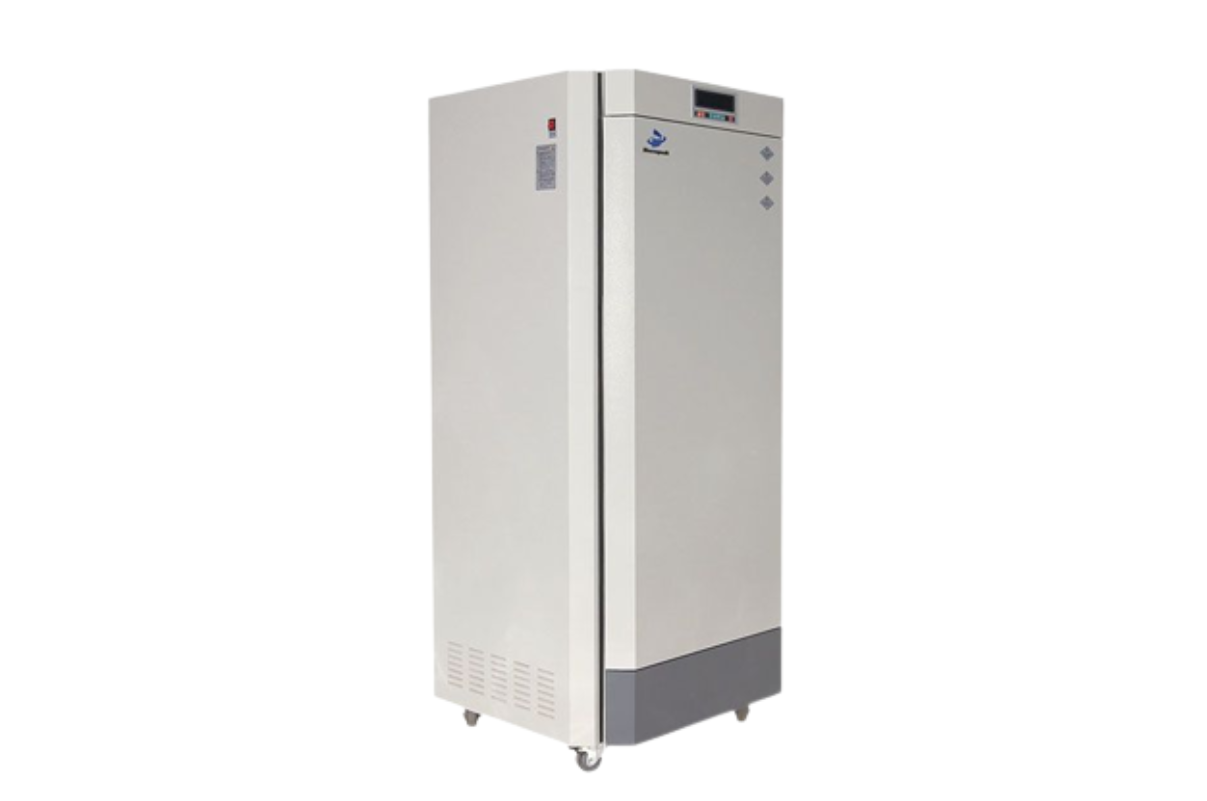

54. Plant Growth Chamber
A plant growth chamber provides a controlled environment in which plants can exist. These chambers make it possible to measure the effects of various environmental characteristics, such as light, temperature, humidity, and other atmospheric conditions, on plant growth and function.
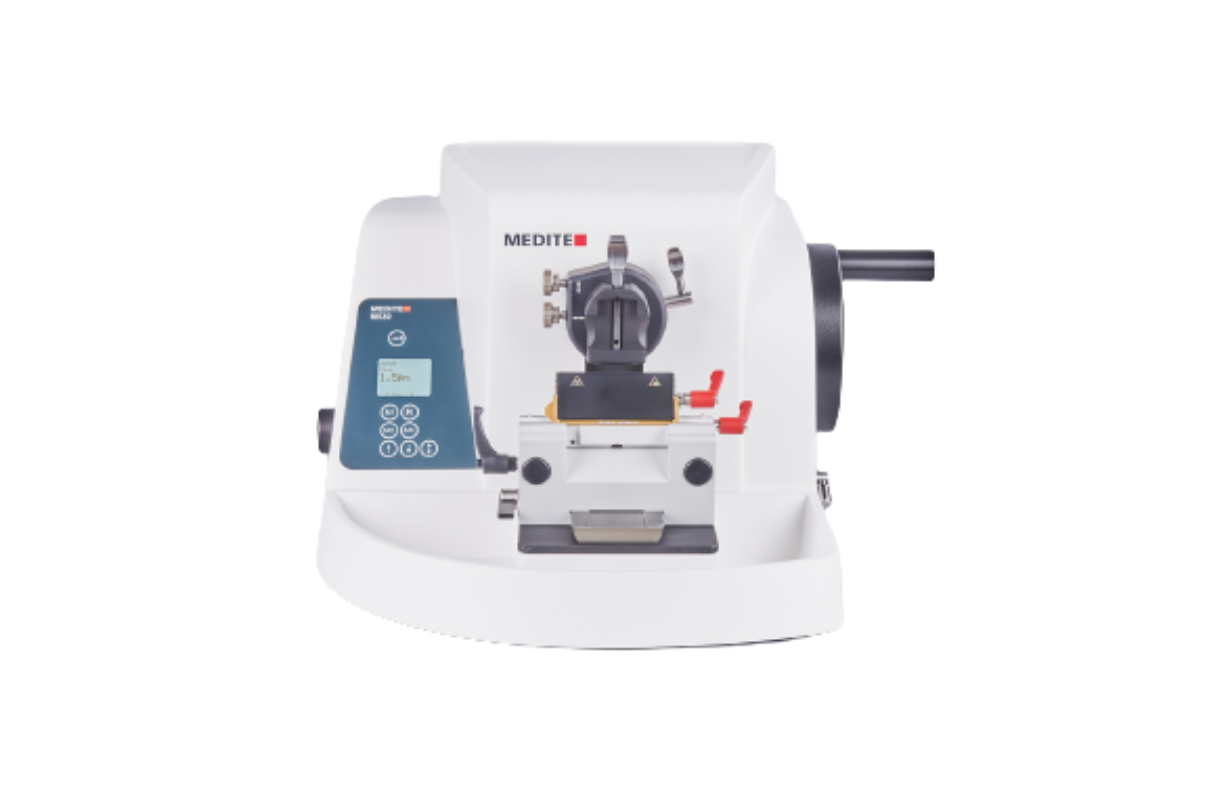

55. Rotary Microtome
The rotary microtome made by microTec is a manually operated cutting device for all types of work with paraffin and hard cutting technology in the field of biology, medicine, and industry. It is used for making microscopic preparations for subsequent illumination (e.g., human tissue).
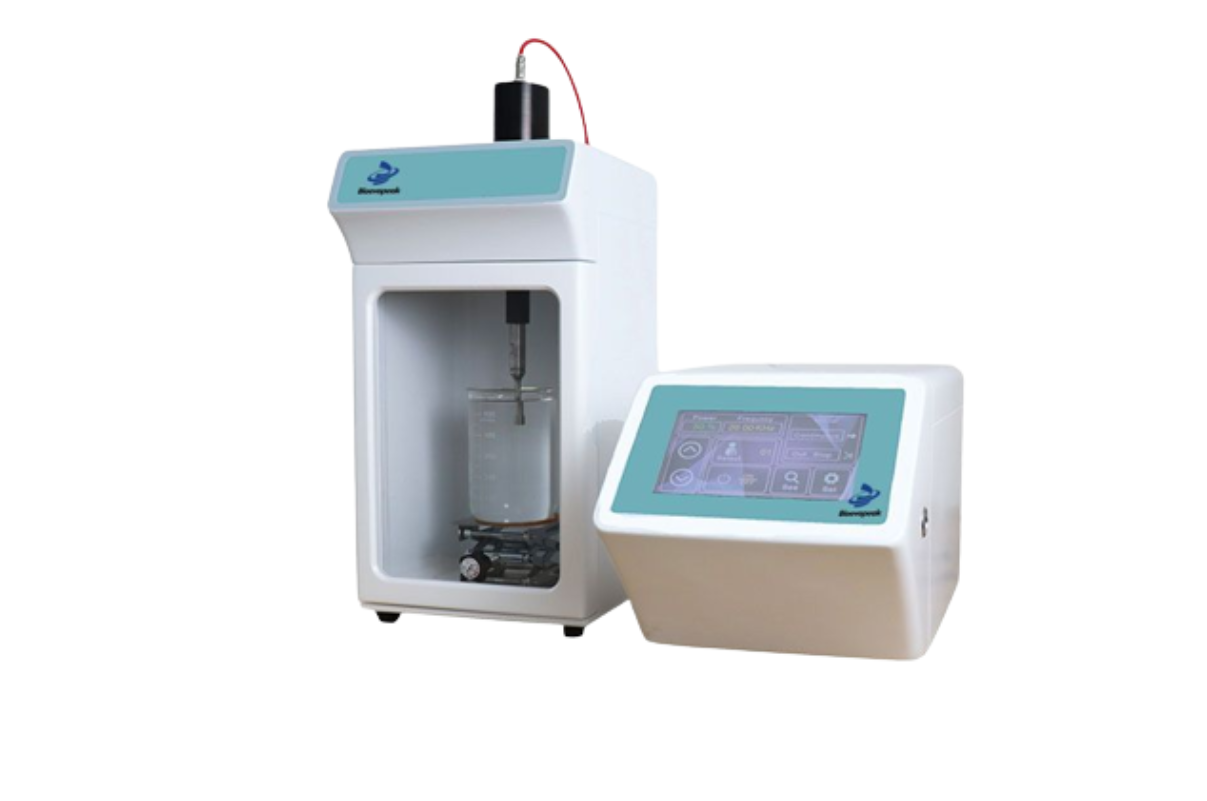

56. Ultrasonic Cell Disruptor
KLB-UH1000 ultrasonic cell disruptor is a multi-functional instrument that can be used for cell disruption and various processes such as emulsification, separation, homogenization, extraction, defoaming, dispersion etc.
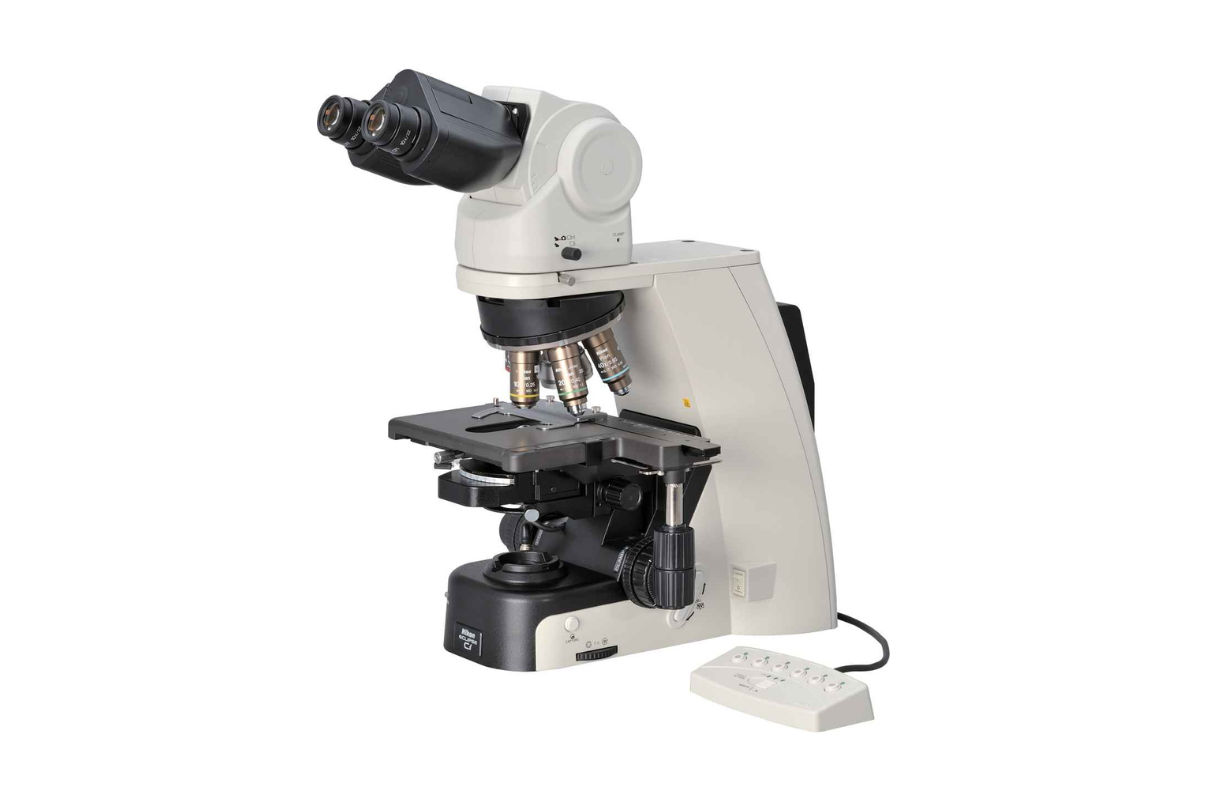

57. Compound Microscope with Fluorescence and Camera attachment
The INFINITY-3-3URC and INFINITY-3-6URC camera models have excellent color reproduction for wide field imaging, while also being sufficiently sensitive to be used for bright fluorescence and allowing a single camera to perform the job typically requiring two separate cameras.
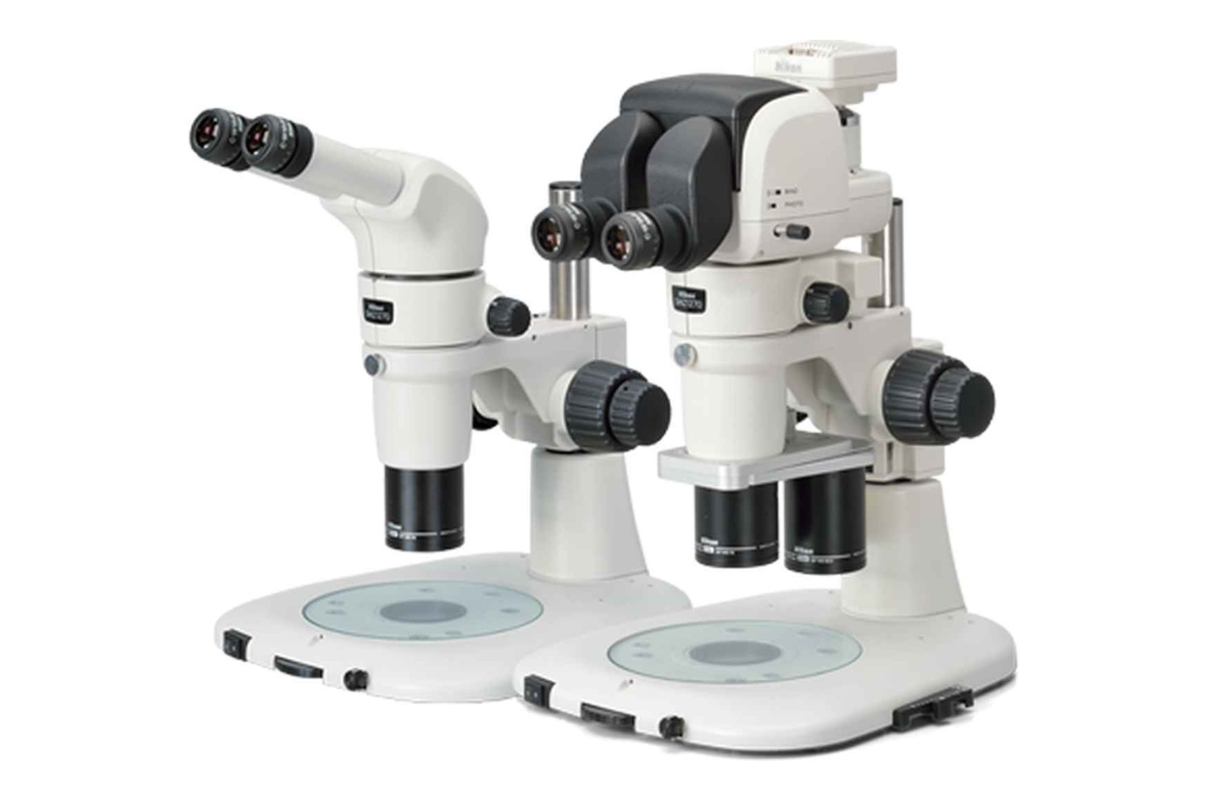

58. Stereo Zoom Microscope with Camera Attachment
Stereo zoom microscopes provide a 3-dimensional or "stereo" image when looking through the microscope. The zoom feature on the stereo zoom microscope provides a range of viewing possibilities, and is the single feature that is most useful when selecting a stereoscope.
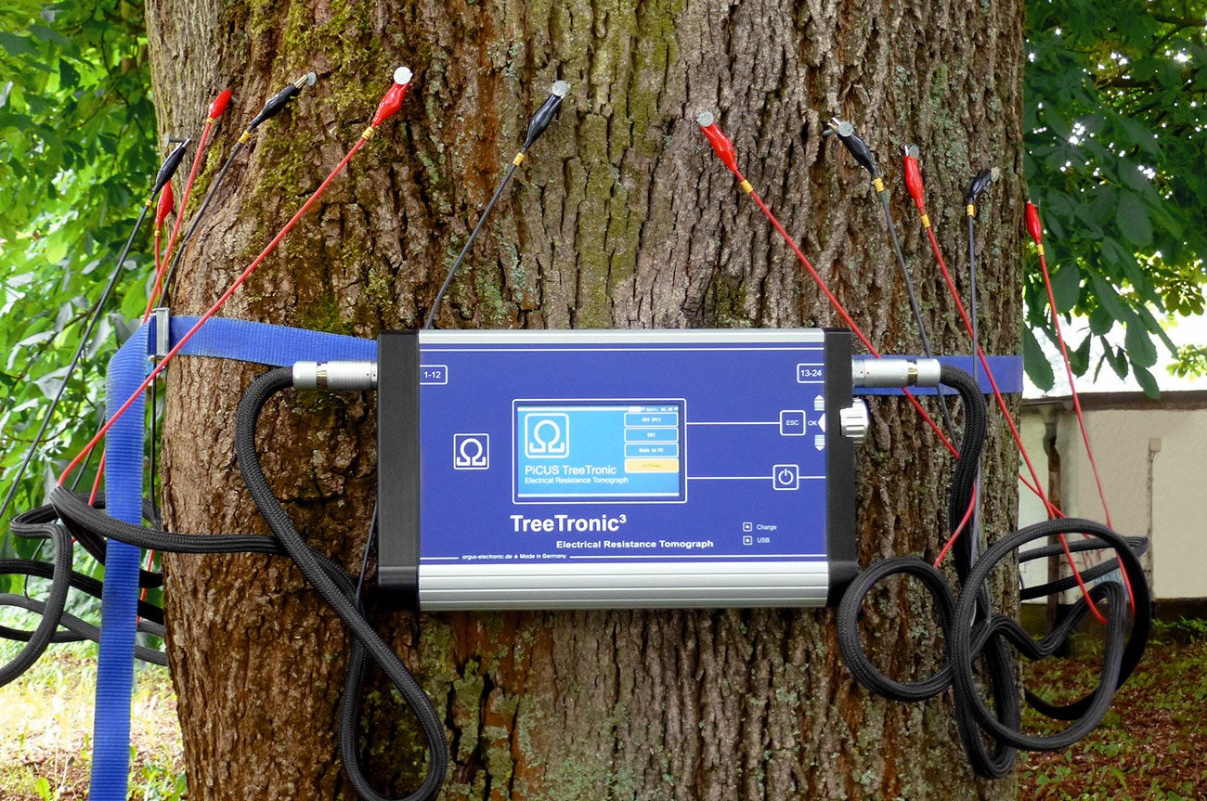

59. Tomographic Equipment for Tree
Sonic tomographs detect decay and cavities in standing trees by measuring the velocity of sound waves in wood. Differences in the velocity can help determine areas of healthy wood and areas of damaged wood that have less elasticity and
60. Single channel pipette (Autoclavable)
The single-channel pipette has one single head to aspirate or dispense very accurate levels of liquid through a disposable tip. They can be used for multiple applications within laboratories which only have a small throughput.
61. Single channel pipette (Non-Autoclavable)
The single-channel pipette allows users to transfer a single aliquot at a time. These tend to be used in laboratories with a low throughput of samples, which can often be those involved in research and development.
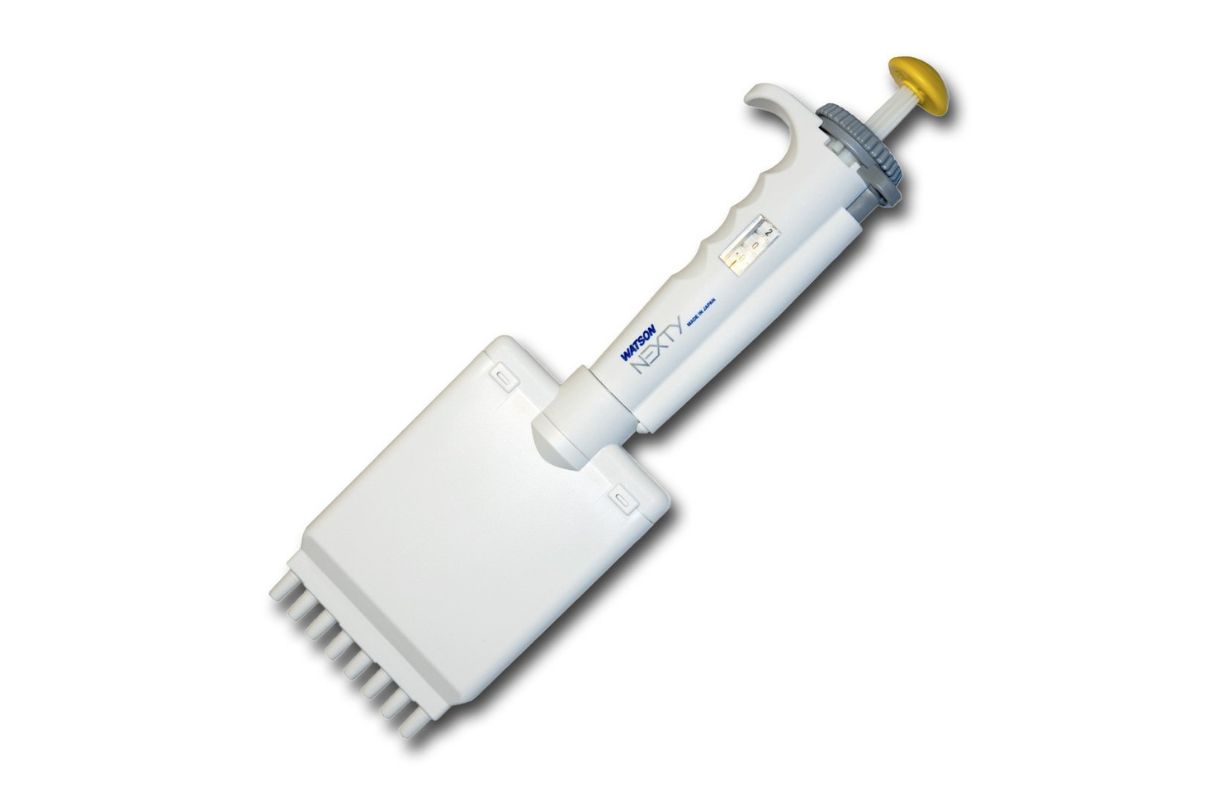

62. Micro Pipette (Eight Channel)
Pipettes are an essential laboratory tool used to dispense measured volumes of liquids. Pipettes most commonly work by creating a partial vacuum above the chamber that holds the liquid and selectively releasing this vacuum to draw up and dispense according to the preferred volume.
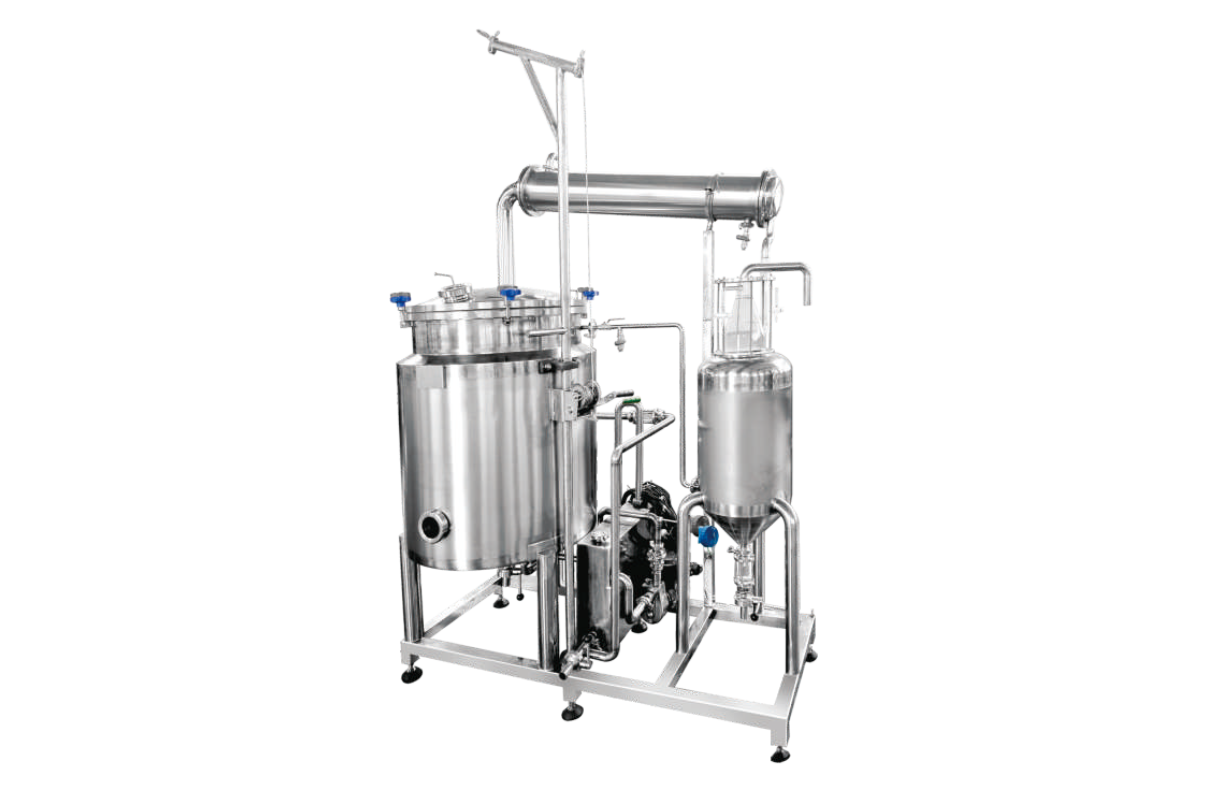

63. Agar oil steam distillation plant with recirculating boiler
In steam distillation, hot steam is forced through the matrix of raw material, opening the cavities in which the oil is held, and volatilizing the oils. This process is, in fact, pure steam distillation. The oil separates from the water in the distillate and is collected.

64. Air cooler: split type 2.5 ton for instrument room
1,201 to 1,500 square feet homes should use 2.5 tons. If your home size is higher than the number above but is less not more than 1,800 square feet, you can go for a three-ton A/C. Choose a unit that is 3.5 tons if your home measures more than 1,800 but not more than 2,100 square feet.
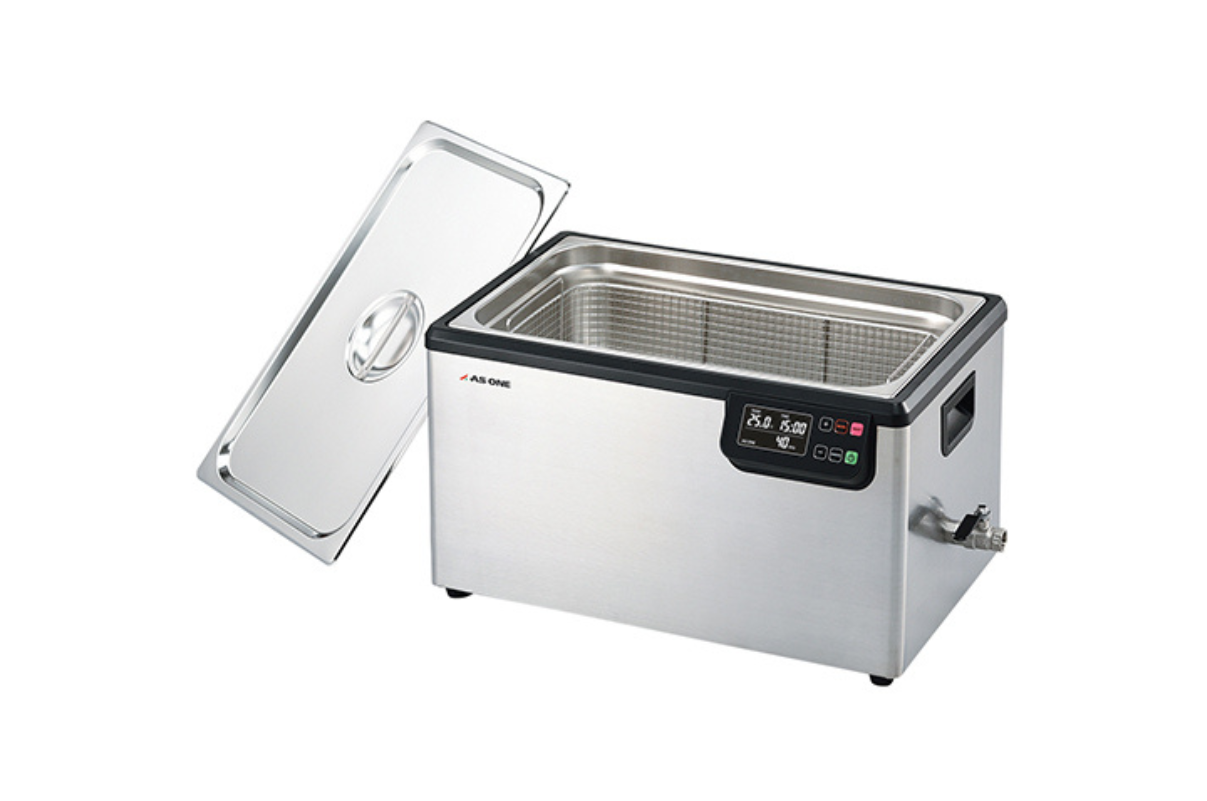

65. Ultrasonic Cleaning Bath (Double Frequency)
While most ultrasonic baths operate at a frequency between 37–45 kHz, you may come across some that operate at a much lower or higher frequency. These Bransonic ultrasonic baths operate at a frequency of 40 kHz.
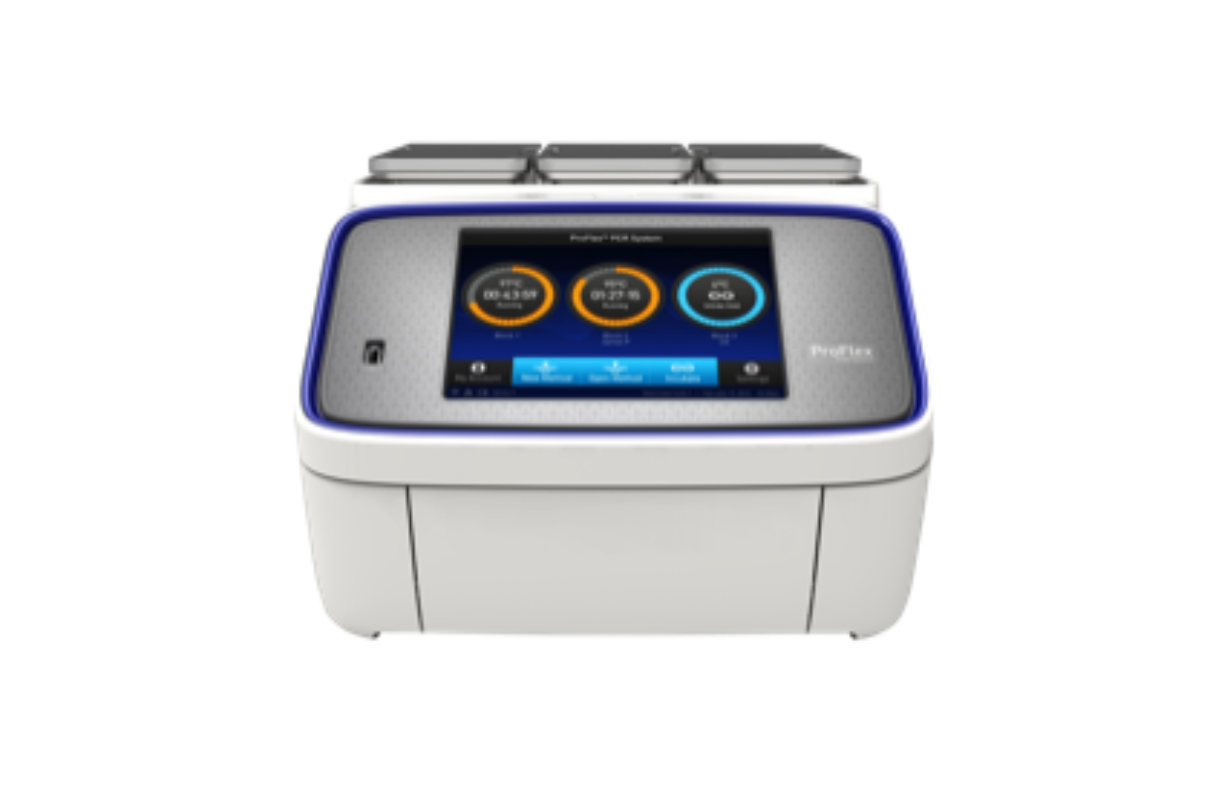

66. Thermal Cycler (Gradient PCR Machine)
Thermocyclers, or polymerase chain reaction (PCR) machines, are laboratory instruments that are used to amplify DNA and RNA samples by the PCR by regulating temperature during cyclical programs.
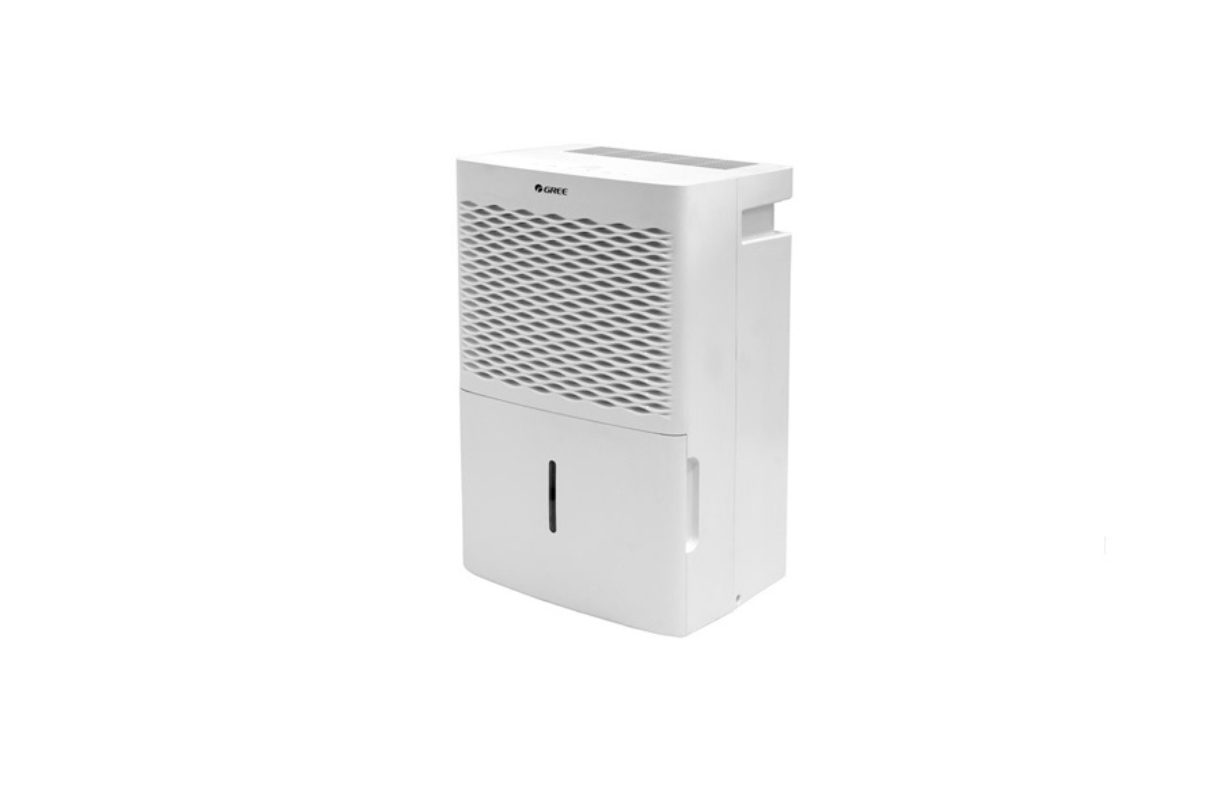

67. Dehumidifier
A dehumidifier removes water from the air in your home until relative humidity is reduced to the level you choose. Once it has reached this level a good dehumidifier should automatically maintain that comfortable level with no interference from you!
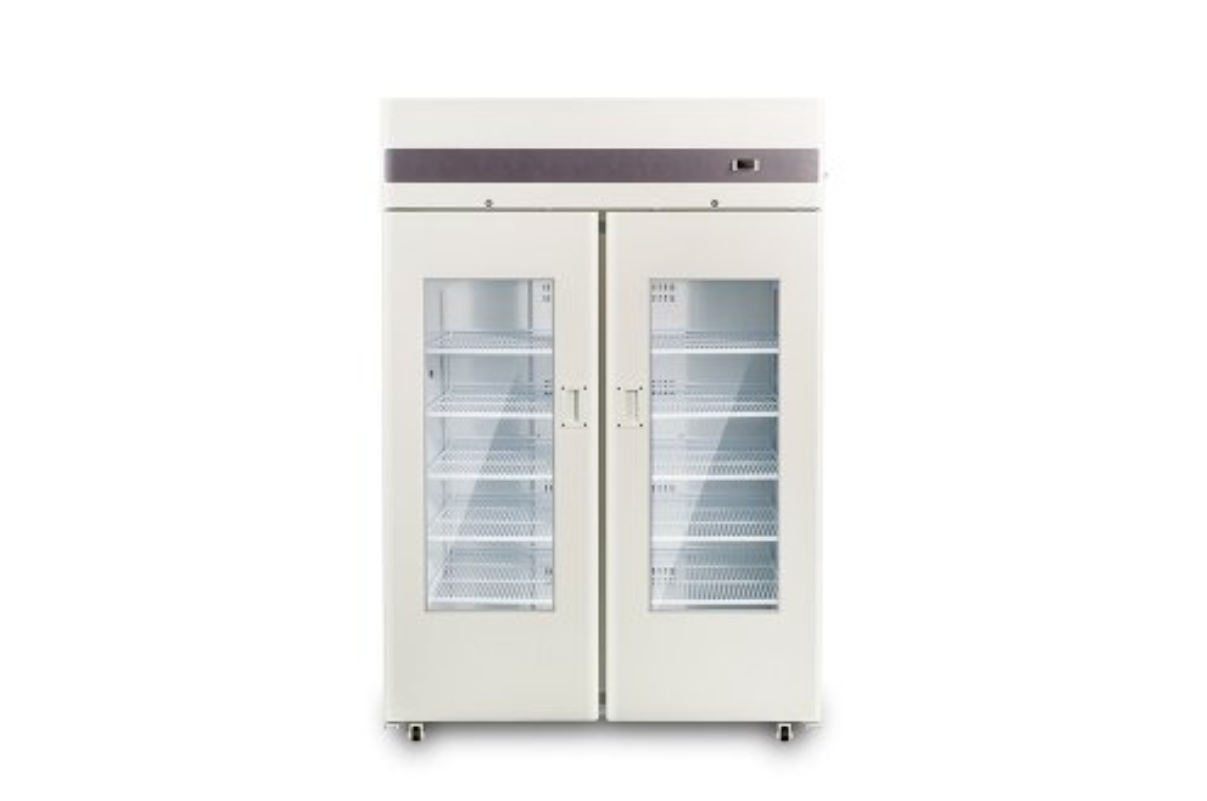

68. Laboratory Freezer
Laboratory freezers are the refrigerated cabinets employed for storing biological samples and reagents in animal laboratories at temperatures ranging from -40oC to 10oC. The purpose of freezing biological samples is to store them for long-term usage without damaging their structural and metabolic integrity.

69. Cooler Box
An electric-powered cool box can be used for a whole host of different things. The most common use is to keep food and drink cool on the go. However, when used as a portable fridge, this type of cooler is also handy for keeping certain medications at the correct temperature when travelling where necessary.
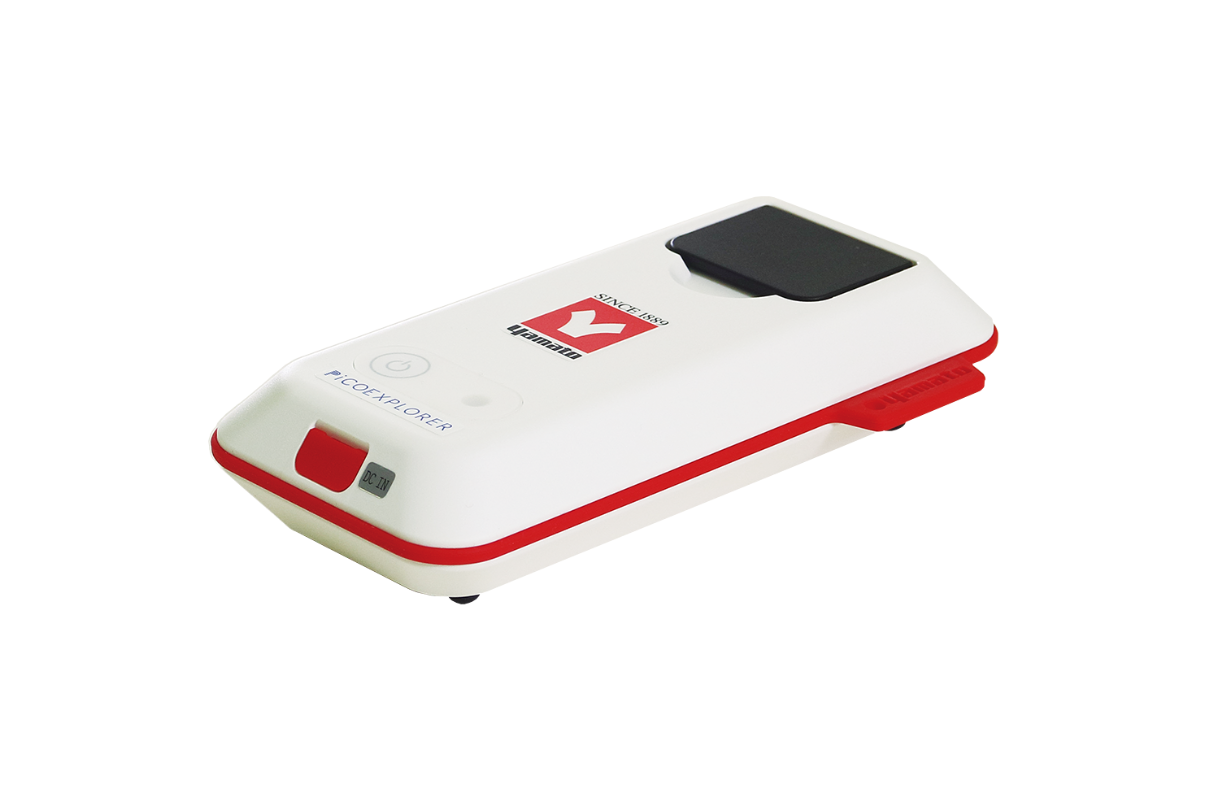

70. Photo Absorbance Meter
A Photo Absorbance Meter, also known as a Spectrophotometer, is a scientific instrument used to measure the absorbance of a sample at specific wavelengths of light. It is widely used in chemistry, biology, and other sciences to analyze light-absorbing substances and determine their concentrations or properties.

71. Demineralized Water Plant
Demineralization is the process of removing mineral salts from Water by using the ion exchange process. Demineralised Water is Water completely free ( or almost ) of dissolved minerals as a result of one of the following processes : Distillation. Deionization.

72. Laboratory Table
During experiments and other laboratory tests, laboratory workbenches are platforms where instruments and equipment are placed. This means that carrying out numerous experiments is nearly difficult without them

73. Reagent Cabinet
From spill containment to segregation from incompatible substances, chemical cabinets reduce the risks associated with hazardous substances. Cabinets are designed for the storage of dangerous goods and hazardous chemicals in the indoor environment.

